Identification of stemness-related glycosylation changes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38600440
- PMCID: PMC11005150
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12161-5
Identification of stemness-related glycosylation changes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Altered glycosylation is a hallmark of cancer associated with therapy resistance and tumor behavior. In this study, we investigated the glycosylation profile of stemness-related proteins OCT4, CIP2A, MET, and LIMA1 in HNSCC tumors.
Methods: Tumor, adjacent normal tissue, and blood samples of 25 patients were collected together with clinical details. After tissue processing, lectin-based glycovariant screens were performed.
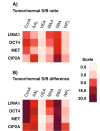
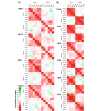
Results: Strong correlation between glycosylation profiles of all four stemness-related proteins was observed in tumor tissue, whereas glycosylation in tumor tissue, adjacent normal tissue, and serum was differential.
Conclusions: A mannose- and galactose-rich glycosylation niche associated with stemness-related proteins was identified.
Keywords: Bioaffinity assay; Glycosylation; HNSCC; Lectin; Stemness.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by other authors.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

