Formation of Anisotropic Conducting Interlayer for High-Resolution Epidermal Electromyography Using Mixed-Conducting Particulate Composite
- PMID: 38600655
- PMCID: PMC11251554
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202308014
Formation of Anisotropic Conducting Interlayer for High-Resolution Epidermal Electromyography Using Mixed-Conducting Particulate Composite
Abstract
Epidermal electrophysiology is a non-invasive method used in research and clinical practices to study the electrical activity of the brain, heart, nerves, and muscles. However, electrode/tissue interlayer materials such as ionically conducting pastes can negatively affect recordings by introducing lateral electrode-to-electrode ionic crosstalk and reducing spatial resolution. To overcome this issue, biocompatible, anisotropic-conducting interlayer composites (ACI) that establish an electrically anisotropic interface with the skin are developed, enabling the application of dense cutaneous sensor arrays. High-density, conformable electrodes are also microfabricated that adhere to the ACI and follow the curvilinear surface of the skin. The results show that ACI significantly enhances the spatial resolution of epidermal electromyography (EMG) recording compared to conductive paste, permitting the acquisition of single muscle action potentials with distinct spatial profiles. The high-density EMG in developing mice, non-human primates, and humans is validated. Overall, high spatial-resolution epidermal electrophysiology enabled by ACI has the potential to advance clinical diagnostics of motor system disorders and enhance data quality for human-computer interface applications.
Keywords: EMG; anisotropic conductors; conducting polymers; organic bioelectronics.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
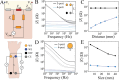
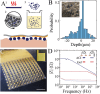

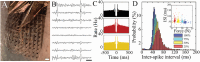

References
-
- Geselowitz D. B., Proceedings of the IEEE 1989, 77, 857.
-
- Kamen G., Caldwell G. E., J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 13, 366. - PubMed
-
- Teplan M., Measurement Science Review 2002, 2, 1.
-
- Jastrzebska‐Perfect P., Chowdhury S., Spyropoulos G. D., Zhao Z., Cea C., Gelinas J. N., Khodagholy D., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909165.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
