A Systematic Review on the Mental Health Status of Patients Infected With Monkeypox Virus
- PMID: 38601106
- PMCID: PMC11001497
- DOI: 10.5765/jkacap.230064
A Systematic Review on the Mental Health Status of Patients Infected With Monkeypox Virus
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to extract and summarize the literature on the mental health status of patients with monkeypox.
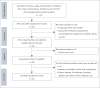
Methods: This review was carried out according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines using different databases and publishers such as Scopus, Sage, ScienceDirect, PubMed, BMJ, Wiley Online Library, Wolters Kluwer OVID-SP, and Google Scholar. The literature review was based on monkeypox and mental health. The year of publication was 2021-2023, during the monkeypox disease period. Data were extracted from opinions, editorials, empirical studies, and surveys.
Results: Based on the literature related to the mental status of patients with monkeypox, the following themes and subthemes were identified: anxiety and depression, self-harm and suicidal tendencies, neuropsychiatric symptoms, mental health, social stigma, sex workers, vaccination, and stress-related diseases.
Conclusion: A review of monkeypox virus infection studies reveals that 25%-50% of patients experience anxiety and depression due to isolation, boredom, and loneliness. Factors such as infected people, a lack of competence among healthcare professionals, and shame over physical symptoms exacerbate mental insults. The implications of society include increased self-harm, suicide, low productivity, fear of stigmatization, and transmission of infection.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Mental stress; Monkeypox; Suicide.
Copyright © 2024 Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between humiliation, shame, self-harm and suicidal behaviours among adolescents and young adults: A systematic review protocol.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 23;17(11):e0278122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278122. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36417449 Free PMC article.
-
HIV related stigma associated with social support, alcohol use disorders, depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among people living with HIV: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022 Mar 4;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13033-022-00527-w. Int J Ment Health Syst. 2022. PMID: 35246211 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Evaluation of the Use of Digital Mental Health Platforms and Interventions: Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 26;20(1):362. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010362. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612685 Free PMC article.
-
The Changing Global Epidemiology of Re-emerging Human Monkeypox Virus Infection: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 12;15(9):e45123. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45123. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37842498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mental health implication of mpox: Enhancing care with genetic insights.J Public Health Afr. 2025 Jan 24;16(1):786. doi: 10.4102/jphia.v16i1.786. eCollection 2025. J Public Health Afr. 2025. PMID: 39968354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control, author. 2022-2023 Mpox outbreak global map [Internet] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA: [cited 2023 Nov 23]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/response/2022/world-map.html .
-
- Daskalakis D, McClung RP, Mena L Daskalakis D, McClung RP, Mena L, Mermin J, author; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Monkeypox Response Team, author. Monkeypox: avoiding the mistakes of past infectious disease epidemics. Ann Intern Med. 2022;175:1177–1178. doi: 10.7326/M22-1748. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources