Effect of dietary supplementation Ampelopsis grossedentata extract on growth performance and muscle nutrition of Megalobrama hoffmanni by gut bacterial mediation
- PMID: 38601588
- PMCID: PMC11004802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29008
Effect of dietary supplementation Ampelopsis grossedentata extract on growth performance and muscle nutrition of Megalobrama hoffmanni by gut bacterial mediation
Abstract
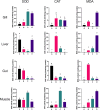
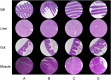
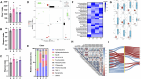
Nowadays, Megalobrama hoffmanni is a typical cultured fish in south China due to its resource decline in the Pearl River. Meanwhile, since antibiotics had been banned internationally, Chinese medical herbal plant serving as alternative to antibiotics has been adopted in aquaculture. In the present study, to ensure the health growth of M. hoffmanni, extract of traditional medical herbal plant Ampelopsis grossedentata was dietary supplemented and a series experiments were performed, including growth performance determination, physiological/biochemical detection, nutrition analysis, histology analysis, and 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Growth performance enhancement was determined since the weight gain rate (WGR), specific growth rate (SGR), and condition factor (CF) of M. hoffmanni increased as feeding inclusion A. grossedentata extract. Interestingly, the total content of muscle fatty acids ascended via supplementing A. grossedentata extract at middle level, in which group the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) significantly increased and thus retarded the lipid peroxidation process (manifesting as malondialdehyde (MDA) content rising). Additionally, immune response and inflammatory reaction was stimulated in low and high level A. grossedentata extract added groups, indicating a suitable dosage of A. grossedentata extract benefited in safety production. Moreover, gut microbiota community varied hugely as daily supplementation A. grossedentata extract and the keystone species were tightly related to lipid transformation, which ultimately led to fatty acids composition variation. Our results confirmed that dietary supplementation A. grossedentata extract at the middle level (0.5‰, w/w) is suitable for serving as feed additive in healthful aquaculture of M. hoffmanni.
Keywords: Ampelopsis grossedentata extract; Fatty acids; Growth performance; Gut microbiota; Megalobrama hoffmanni.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Luo Y.L. A revision of fishes of the cyprinid genus Megalobrama. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 1990;14:160–165.
-
- Song W., Wang Y.Z., Zhu D.M., Ren L. Morphological variations among the genus Megalobrama. Freshw. Fish. 2013;43:21–27.
-
- Chen J., Li F.G., Huang C.X., et al. Morphological variations of genera Parabramis and Megalobrama teleost populations. Journal of Shanghai University. 2014;23:388–394.
-
- Li S.F., Zhu Z.W., Zou S.M., et al. Interspecific phylogenesis and intraspecific genetic differences of genus Megalobrama: bluntnose black bream (M. amblycephala), guangdong black bream (M. hoffmanni) and black bream (M. terminalis) Acta Zool. Sin. 2001;48:339–345.
-
- Sun X., Guo L., Luo D., et al. Long-term increase in mortality of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in the Pearl River Estuary following anthropic activities: evidence from the stranded dolphin mortality analysis from 2003 to 2017. Environ. Pollut. 2022;307 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

