The impact of adapted exercises in basketball on the perception of the difficulty and physical enjoyment of students with overweight
- PMID: 38601694
- PMCID: PMC11004205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29190
The impact of adapted exercises in basketball on the perception of the difficulty and physical enjoyment of students with overweight
Abstract
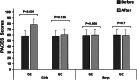
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of the adapted basketball cycle on the perceived level of difficulty and physical enjoyment in girls and boys with overweight. Sixty-six students with overweight (aged 16-18 years) were randomly assigned to an experimental group (EG, n = 32 including 20 boys and 12 girls) and a control group (CG, n = 34; including 21 boys and 13 girls). Statistical analysis also showed that the levels of perceived difficulty decreased significantly after of seven-week of the adapted basketball cycle in both boys (Δ% = - 0.27; p < 0.001; and girls (Δ% = - 0.36; p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in students who participated in the traditional basketball cycle. A physical activity enjoyment Scale revealed that in girls, the level of enjoyment increased significantly (Δ% = + 0.27; P < 0.001) after an adapted basketball cycle. There was no significant change in physical enjoyment in boys EG (P = 0.808) and participants in the control groups. These results push us to opt more for adapted and motivational learning situations to make the teaching-learning process better, in students with overweight.
Keywords: Adapting; Basketball; Overweight: difficulty; Perception; Physical enjoyment.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. No funding was received for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Tanveer M., Hohmann A., Roy N., Zeba A., Tanveer U., Siener M. The current prevalence of underweight, overweight, and obesity associated with demographic factors among Pakistan school-aged children and adolescents-an empirical cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2022;19(18) doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811619. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zemene M.A., Anley D.T., Gebeyehu N.A., Adella G.A., Kassie G.A., Mengstie M.A., Seid M.A., Abebe E.C., Gesese M.M., Tesfa N.A., Kebede Y.S., Bantie B., Feleke S.F., Dejenie T.A., Bayeh W.A., Dessie A.M. Concurrent stunting and overweight or obesity among under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa: a multilevel analysis. Arch. Publ. Health. 2023;81(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13690-023-01138-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Esteban C., Antón-Ladislao A., Aramburu A., Chasco L., Orive M., Sobradillo P., López-Roldan L., Jiménez-Puente A., de Miguel J., García-Talavera I., Quintana J.M., ReEPOC-REDISSEC group Physical activity and sedentary behaviour in patients admitted with COPD: associated factors. Respiratory Medicine Research. 2023;84 doi: 10.1016/j.resmer.2023.101052. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

