Lacticaseibacillusparacasei BNCC345679 revolutionizes DSS-induced colitis and modulates gut microbiota
- PMID: 38601942
- PMCID: PMC11004379
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1343891
Lacticaseibacillusparacasei BNCC345679 revolutionizes DSS-induced colitis and modulates gut microbiota
Abstract
The gut microbiota plays an important role in the disease progression of inflammatory bowel disease. Although probiotics are effective against IBD, not many studies have investigated their effects on gut microbiota composition and immunomodulation in mouse colitis models. Our study aimed at the therapeutic effects of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei BNCC345679 for the first time and explored its impact on gut microbiome dysbiosis, inflammatory cytokines, related miRNAs, VCAM-1, oxidative stress, intestinal integrity, and mucus barrier. We found that oral intervention of L. paracasei BNCC345679 affects recovering beneficial microbial taxa, including lactobacillus spp. and akkermansia spp., followed by improved body weight, DAI score, and inflammatory cytokines. L. paracasei BNCC345679 mitigated oxidative stress and increased the expression of intestinal integrity proteins MUC2 and ZO-1. These results suggested that L. paracasei BNCC345679 has the capacity to reduce DSS-induced colitis and has the potential as a supplement for the mitigation of IBD.
Keywords: DSS-induced colitis; Lacticaseibacillus paracasei BNCC345679; dysbiosis; gut inflammation; gut microbiota; microRNA; probiotics.
Copyright © 2024 Ahmad, Din, Khan, Rehman, Hassan, Aziz, Alharbi and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
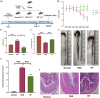

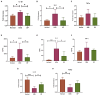

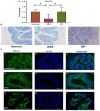
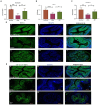


References
-
- Alemany-Cosme E., Sáez-González E., Moret I., Mateos B., Iborra M., Nos P., et al. . (2021). Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease and the interconnection with immunological response, microbiota, external environmental factors, and epigenetics. Antioxidants (Basel) 10:64. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010064, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Algieri F., Garrido-Mesa J., Vezza T., Rodríguez-Sojo M. J., Rodríguez-Cabezas M. E., Olivares M., et al. . (2021). Intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics in DNBS-colitis via modulation of gut microbiota and microRNAs. Eur. J. Nutr. 60, 2537–2551. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02441-8, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aziz T., Khan A. A., Tzora A., Voidarou C. C., Skoufos I. (2023). Dietary implications of the bidirectional relationship between the gut microflora and inflammatory diseases with special emphasis on irritable bowel disease: current and future perspective. Nutrients 15:956. doi: 10.3390/nu15132956, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

