Endothelial Cell Flow-Mediated Quiescence Is Temporally Regulated and Utilizes the Cell Cycle Inhibitor p27
- PMID: 38602102
- PMCID: PMC11238946
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320671
Endothelial Cell Flow-Mediated Quiescence Is Temporally Regulated and Utilizes the Cell Cycle Inhibitor p27
Abstract
Background: Endothelial cells regulate their cell cycle as blood vessels remodel and transition to quiescence downstream of blood flow-induced mechanotransduction. Laminar blood flow leads to quiescence, but how flow-mediated quiescence is established and maintained is poorly understood.
Methods: Primary human endothelial cells were exposed to laminar flow regimens and gene expression manipulations, and quiescence depth was analyzed via time-to-cell cycle reentry after flow cessation. Mouse and zebrafish endothelial expression patterns were examined via scRNA-seq (single-cell RNA sequencing) analysis, and mutant or morphant fish lacking p27 were analyzed for endothelial cell cycle regulation and in vivo cellular behaviors.
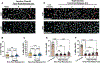
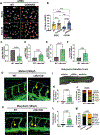
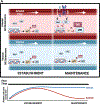
Results: Arterial flow-exposed endothelial cells had a distinct transcriptome, and they first entered a deep quiescence, then transitioned to shallow quiescence under homeostatic maintenance conditions. In contrast, venous flow-exposed endothelial cells entered deep quiescence early that did not change with homeostasis. The cell cycle inhibitor p27 (CDKN1B) was required to establish endothelial flow-mediated quiescence, and expression levels positively correlated with quiescence depth. p27 loss in vivo led to endothelial cell cycle upregulation and ectopic sprouting, consistent with loss of quiescence. HES1 and ID3, transcriptional repressors of p27 upregulated by arterial flow, were required for quiescence depth changes and the reduced p27 levels associated with shallow quiescence.
Conclusions: Endothelial cell flow-mediated quiescence has unique properties and temporal regulation of quiescence depth that depends on the flow stimulus. These findings are consistent with a model whereby flow-mediated endothelial cell quiescence depth is temporally regulated downstream of p27 transcriptional regulation by HES1 and ID3. The findings are important in understanding endothelial cell quiescence misregulation that leads to vascular dysfunction and disease.
Keywords: blood circulation; cell cycle; cell cycle checkpoints; endothelial cells; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Update of
-
Endothelial cell flow-mediated quiescence is temporally regulated and utilizes the cell cycle inhibitor p27.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 4:2023.06.09.544403. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.09.544403. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Jun;44(6):1265-1282. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320671. PMID: 37662222 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Endothelial cell flow-mediated quiescence is temporally regulated and utilizes the cell cycle inhibitor p27.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 4:2023.06.09.544403. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.09.544403. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Jun;44(6):1265-1282. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320671. PMID: 37662222 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Endothelial Cell Transcriptome Heterogeneity Under Homeostatic Laminar Flow.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Oct;41(10):2575-2584. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316797. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 34433297 Free PMC article.
-
DLL4/Notch1 and BMP9 Interdependent Signaling Induces Human Endothelial Cell Quiescence via P27KIP1 and Thrombospondin-1.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Dec;35(12):2626-37. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306541. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26471266 Free PMC article.
-
p27(Kip1) is required to maintain proliferative quiescence in the adult cochlea and pituitary.Cell Cycle. 2011 Apr 15;10(8):1237-48. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15301. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21403466 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of p27 in cell cycle, apoptosis, epigenetic modification and transcriptional regulation for the control of cell growth: A double-edged sword protein.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Sep;69:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Jul 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30075372 Review.
Cited by
-
Quiescence-Origin Senescence: A New Paradigm in Cellular Aging.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 13;12(8):1837. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081837. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200301 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling of self-assembled microvascular networks under long term flow.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 18:2025.03.17.643791. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.17.643791. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40166169 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Same same but different? How blood and lymphatic vessels induce cell contact inhibition.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Feb 6;53(1):BST20240573. doi: 10.1042/BST20240573. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 39912714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levesque MJ, Sprague EA, Schwartz CJ, Nerem RM. The Influence of Shear Stress on Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells: The Stress Response of an Anchorage-Dependent Mammalian Cell. Biotechnol Prog. 1989;5:1–8. doi:10.1002/btpr.5420050105 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

