Prediction of trends in unfavorable prognosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke according to low left ventricular ejection fraction levels
- PMID: 38603602
- PMCID: PMC11529670
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X241247020
Prediction of trends in unfavorable prognosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke according to low left ventricular ejection fraction levels
Abstract
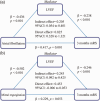
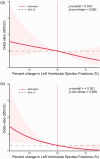
As few studies have reported the impact of lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) on the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients, we aimed to explore this through a retrospective cohort study and a meta-analysis. A total of 283 AIS patients receiving intravenous thrombolysis at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University between 2016 and 2019 were enrolled and divided into three groups based on LVEF tertiles. The logistic regression model estimated the association between LVEF and the three-month AIS prognosis. After adjusting for confounding factors, patients in tertile 3 exhibited an increased risk of poor functional outcome and mortality [odds ratio (OR), 2.656 (95% CI: 1.443-4.889); OR, 7.586 (95% CI: 2.102-27.375)]. A systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane Library was performed. Our meta-analysis revealed that LVEF < 40% was significantly associated with poor functional outcome [OR 1.94 (95% CI: 1.08-3.50)], mortality [OR 3.69 (95% CI: 1.22-11.11)], as well as LVEF < 55% [OR 1.68 (95% CI: 1.22-2.32); 2.27 (95% CI: 1.30-3.96)], respectively. A decreased LVEF could predict an inferior prognosis for AIS; therefore, it could aid in clinical decision-making in this patient population.
Keywords: Left ventricular ejection fraction; acute ischemic stroke; cardioembolic stroke; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction predicts clinical prognosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke after intravenous thrombolysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 2;16(9):7845-7855. doi: 10.18632/aging.205786. Epub 2024 May 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38700495 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of Ratio of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction to Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure to Long-Term Prognosis After ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Jan 15;123(2):199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30424868
-
Effect of left ventricular ejection fraction Spectrum on 1-Year mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Nov;29(11):3518-3527. doi: 10.1111/cns.14285. Epub 2023 Jun 7. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287419 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Physiologic Pacing Versus Right Ventricular Pacing Among Patients With Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Greater Than 35%: A Systematic Review for the 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline on the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Bradycardia and Cardiac Conduction Delay: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society.Circulation. 2019 Aug 20;140(8):e483-e503. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000629. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30586773
-
Left ventricular systolic function evaluated by strain echocardiography and relationship with mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2018 Aug 4;22(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2113-y. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30075792 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation study of CAR, PLR, NLR with the prognosis of cardiogenic cerebral embolism patients.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025 Jun 17;250:10517. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2025.10517. eCollection 2025. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2025. PMID: 40599820 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal Single Subcortical Infarction, Left Ventricular Fractional Shortening, and Risk Prediction Model Development for Neurological Deterioration in Patients With Anterior Circulation Single Subcortical Infarction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 May 20;14(10):e040337. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.040337. Epub 2025 May 13. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40357665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al.. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1317–1329. - PubMed
-
- Prabhakaran S, Ruff I, Bernstein RA. Acute stroke intervention: a systematic review. JAMA 2015; 313: 1451–1462. - PubMed
-
- Doehner W, Ural D, Haeusler KG, et al.. Heart and brain interaction in patients with heart failure: overview and proposal for a taxonomy. A position paper from the study group on heart and brain interaction of the heart failure association. Eur J Heart Fail 2017; 20: 199–215. - PubMed
-
- Erkelens CD, van der Wal HH, de Jong BM, et al.. Dynamics of cerebral blood flow in patients with mild non-ischaemic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2017; 19: 261–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

