House dust-derived mixtures of organophosphate esters alter the phenotype, function, transcriptome, and lipidome of KGN human ovarian granulosa cells
- PMID: 38603619
- PMCID: PMC11199920
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae052
House dust-derived mixtures of organophosphate esters alter the phenotype, function, transcriptome, and lipidome of KGN human ovarian granulosa cells
Abstract
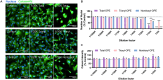
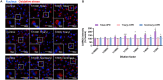
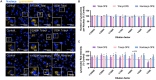
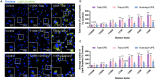
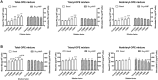
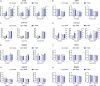
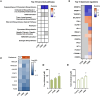
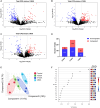
Organophosphate esters (OPEs), used as flame retardants and plasticizers, are present ubiquitously in the environment. Previous studies suggest that exposure to OPEs is detrimental to female fertility in humans. However, no experimental information is available on the effects of OPE mixtures on ovarian granulosa cells, which play essential roles in female reproduction. We used high-content imaging to investigate the effects of environmentally relevant OPE mixtures on KGN human granulosa cell phenotypes. Perturbations to steroidogenesis were assessed using ELISA and qRT-PCR. A high-throughput transcriptomic approach, TempO-Seq, was used to identify transcriptional changes in a targeted panel of genes. Effects on lipid homeostasis were explored using a cholesterol assay and global lipidomic profiling. OPE mixtures altered multiple phenotypic features of KGN cells, with triaryl OPEs in the mixture showing higher potencies than other mixture components. The mixtures increased basal production of steroid hormones; this was mediated by significant changes in the expression of critical transcripts involved in steroidogenesis. Further, the total-OPE mixture disrupted cholesterol homeostasis and the composition of intracellular lipid droplets. Exposure to complex mixtures of OPEs, similar to those found in house dust, may adversely affect female reproductive health by altering a multitude of phenotypic and functional endpoints in granulosa cells. This study provides novel insights into the mechanisms of actions underlying the toxicity induced by OPEs and highlights the need to examine the effects of human relevant chemical mixtures.
Keywords: high-content imaging; high-throughput transcriptomics; lipidomics; mixture; organophosphate esters; ovarian granulosa cells.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenotypic and Functional Outcomes in Macrophages Exposed to an Environmentally Relevant Mixture of Organophosphate Esters in Vitro.Environ Health Perspect. 2024 Aug;132(8):87002. doi: 10.1289/EHP13869. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Environ Health Perspect. 2024. PMID: 39115886 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exposure to a Mixture of Organophosphate Esters on Adrenal Cell Phenotype, Lipidome, and Function.Endocrinology. 2024 Feb 20;165(4):bqae024. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae024. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38376928 Free PMC article.
-
Organophosphate Esters Disrupt Steroidogenesis in KGN Human Ovarian Granulosa Cells.Endocrinology. 2023 Jun 6;164(7):bqad089. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad089. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37288667 Free PMC article.
-
Organophosphate Esters: Are These Flame Retardants and Plasticizers Affecting Children's Health?Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019 Dec;6(4):201-213. doi: 10.1007/s40572-019-00258-0. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019. PMID: 31755035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: Levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions.Environ Int. 2019 Jun;127:35-51. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 30901640 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicity Assessment of Organophosphate Flame Retardants Using New Approach Methodologies.Toxics. 2025 Apr 11;13(4):297. doi: 10.3390/toxics13040297. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40278613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of exposure to a mixture of organophosphate esters on the adrenal glands of Sprague Dawley rats.Toxicol Sci. 2025 Mar 1;204(1):43-56. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae154. Toxicol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39658253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aluru N., Hallanger I. G., McMonagle H., Harju M. (2021). Hepatic gene expression profiling of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) liver after exposure to organophosphate flame retardants revealed altered cholesterol biosynthesis and lipid metabolism. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 40, 1639–1648. - PubMed
-
- An J., Jiang J., Tang W., Zhong Y., Ren G., Shang Y., Yu Z. (2023). Lipid metabolic disturbance induced by triphenyl phosphate and hydroxy metabolite in HepG2 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 262, 115160. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

