Development of a prognostic risk score to predict early mortality in incident elderly Japanese hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 38603695
- PMCID: PMC11008820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302101
Development of a prognostic risk score to predict early mortality in incident elderly Japanese hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Information of short-term prognosis after hemodialysis (HD) introduction is important for elderly patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and their families choosing a modality of renal replacement therapy. Therefore, we developed a risk score to predict early mortality in incident elderly Japanese hemodialysis patients.
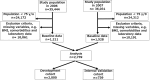
Materials and methods: We analyzed data of incident elderly HD patients from a nationwide cohort study of the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy Renal Data Registry (JRDR) to develop a prognostic risk score. Candidate risk factors for early death within 1 year was evaluated using multivariate logistic regression analysis. The risk score was developed by summing up points derived from parameter estimate values of independent risk factors. The association between risk score and early death was tested using Cox proportional hazards models. This risk score was validated twice by using an internal validation cohort derived from the JRDR and an external validation cohort collected for this study.
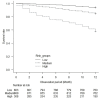
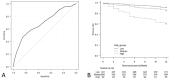
Results: Using the development cohort (n = 2,000), nine risk factors were retained in the risk score: older age (>85), yes = 2, no = 0; sex, male = 2, female = 0; lower body mass index (<20), yes = 2, no = 0; cancer, yes = 1, no = 0; dementia, yes = 3, no = 0; lower creatinine (<6.5 mg/dL), yes = 1, no = 0; lower albumin (<3.0 g/dL), yes = 3, no = 0; normal or high calcium (≥8.5 mg/dL), yes = 1, no = 0; and higher C reactive protein (>2.0 mg/dL), yes = 2, no = 0. In the internal and external validation cohorts (n = 739, 140, respectively), the medium- and high-risk groups (total score, 6 to 10 and 11 or more, respectively) showed significantly higher risk of early death than the low-risk group (total score, 0 to 5) (p<0.001).
Conclusion: We developed a prognostic risk score predicting early death within 1 year in incident elderly Japanese HD patients, which may help detect elderly patients with a high-risk of early death after HD introduction.
Copyright: © 2024 Okada et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new nutritional risk index for predicting mortality in hemodialysis patients: Nationwide cohort study.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 28;14(3):e0214524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214524. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30921398 Free PMC article.
-
[Current peritoneal dialysis compared with haemodialysis: medium-term survival analysis of incident dialysis patients in the Canary Islands in recent years].Nefrologia. 2011;31(2):174-84. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2011.Jan.10743. Nefrologia. 2011. PMID: 21461011 Spanish.
-
The association of the difference in hemoglobin levels before and after hemodialysis with the risk of 1-year mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Results from a nationwide cohort study of the Japanese Renal Data Registry.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):e0210533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210533. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30629677 Free PMC article.
-
Charlson Comorbidity Index is a predictor of outcomes in incident hemodialysis patients and correlates with phase angle and hospitalization.Int J Artif Organs. 2004 Apr;27(4):330-6. doi: 10.1177/039139880402700409. Int J Artif Organs. 2004. PMID: 15163067
-
Dialysis Modality and Mortality in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):983-93. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05160514. Epub 2015 May 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25941194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mortality Risk Prediction Models for People With Kidney Failure: A Systematic Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Jan 2;8(1):e2453190. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.53190. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 39752155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain JA, Mooney A, Russon L. Comparison of survival analysis and palliative care involvement in patients aged over 70 years choosing conservative management or renal replacement therapy in advanced chronic kidney disease. Palliat Med. 2013;27: 829–839. doi: 10.1177/0269216313484380 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yazawa M, Kido R, Ohira S, Hasegawa T, Hanafusa N, Iseki K, et al.. Early mortality was highly and strongly associated with functional status in incident Japanese hemodialysis patients: A cohort study of the large national dialysis registry. PLoS One. 2016;11: 1–14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156951 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

