Measurement of Developmental and Behavioral Concerns in Toddlers With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
- PMID: 38603983
- PMCID: PMC11143920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2024.03.014
Measurement of Developmental and Behavioral Concerns in Toddlers With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Abstract
Background: The TAND (Tuberous Sclerosis Complex [TSC]-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders) Checklist was developed as a clinical screener for neurodevelopmental disorders in TSC. Most studies have described patterns in older children and adults. This study sought to better understand behavioral concerns as measured by the TAND Checklist in young children with TSC.
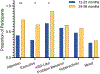
Methods: We examined patterns of caregiver responses to the TAND Checklist in 90 toddlers with TSC (12 to 23 months n = 60; 24 to 36 months n = 30) through data collected during baseline visits across two TSC early intervention studies.
Results: Over 90% of caregivers reported at least one behavioral concern related to TAND. The number of concerns increased with age. Delayed language was the most frequently reported concern across ages (12 to 23 months: 58.3%, 24 to 36 months: 86.7%). Questions related to behavioral concerns were largely relevant in this age range, but questions in other areas, such as neuropsychological or academic function, were not.
Conclusions: TAND symptoms are very common in toddlers with TSC, and these symptoms may increase with age. The TAND Checklist is a useful tool for identifying behavioral concerns efficiently, but several items and sections are not suited to younger children. Results support the development of an abbreviated form of the TAND Checklist for toddlers.
Keywords: Behavioral concerns; TAND; TAND Checklist; TSC-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders; Toddlers; Tuberous sclerosis complex.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Nicole McDonald reports a relationship with TSC Alliance that includes travel reimbursement. Shafali Jeste reports a relationship with TSC Alliance that includes board membership and travel reimbursement. Connie Kasari reports a relationship with TSC Alliance that includes travel reimbursement. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuberous sclerosis-associated neuropsychiatric disorders: a paediatric cohort study.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019 Feb;61(2):168-173. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.14055. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30298907
-
The TAND checklist: a useful screening tool in children with tuberous sclerosis and neurofibromatosis type 1.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Sep 7;15(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01488-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 32894194 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders and Parental Stress: Findings from a National, Prospective TSC Surveillance Study.Neuropediatrics. 2019 Oct;50(5):294-299. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1693042. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Neuropediatrics. 2019. PMID: 31266065
-
[Neuropsychiatric manifestations in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC): diagnostic guidelines, TAND concept and therapy with mTOR inhibitors].Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2019 Mar;47(2):139-153. doi: 10.1024/1422-4917/a000604. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2019. PMID: 30080117 Review. German.
-
International consensus recommendations for the identification and treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex-associated neuropsychiatric disorders (TAND).J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Sep 14;15(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s11689-023-09500-1. J Neurodev Disord. 2023. PMID: 37710171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crino PB. Evolving neurobiology of tuberous sclerosis complex. Acta Neuropathol. 2013; 125(3): 317–332. - PubMed

