Hepatic ketone body regulation of renal gluconeogenesis
- PMID: 38604598
- PMCID: PMC11039402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101934
Hepatic ketone body regulation of renal gluconeogenesis
Abstract
Objectives: During fasting, liver pivotally regulates blood glucose levels through glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Kidney also produces glucose through gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenic genes are transactivated by fasting, but their expression patterns are chronologically different between the two organs. We find that renal gluconeogenic gene expressions are positively correlated with the blood β-hydroxybutyrate concentration. Thus, we herein aim to investigate the regulatory mechanism and its physiological implications.
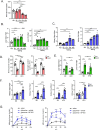
Methods: Gluconeogenic gene expressions in liver and kidney were examined in hyperketogenic mice such as high-fat diet (HFD)-fed and ketogenic diet-fed mice, and in hypoketogenic PPARα knockout (PPARα-/-) mice. Renal gluconeogenesis was evaluated by rise in glycemia after glutamine loading in vivo. Functional roles of β-hydroxybutyrate in the regulation of renal gluconeogenesis were investigated by metabolome analysis and RNA-seq analysis of proximal tubule cells.
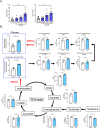
Results: Renal gluconeogenic genes were transactivated concurrently with blood β-hydroxybutyrate uprise under ketogenic states, but the increase was blunted in hypoketogenic PPARα-/- mice. Administration of 1,3-butandiol, a ketone diester, transactivated renal gluconeogenic gene expression in fasted PPARα-/- mice. In addition, HFD-fed mice showed fasting hyperglycemia along with upregulated renal gluconeogenic gene expression, which was blunted in HFD-fed PPARα-/- mice. In vitro experiments and metabolome analysis in renal tubular cells showed that β-hydroxybutyrate directly promotes glucose and NH3 production through transactivating gluconeogenic genes. In addition, RNA-seq analysis revealed that β-hydroxybutyrate-induced transactivation of Pck1 was mediated by C/EBPβ.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that β-hydroxybutyrate mediates hepato-renal interaction to maintain homeostatic regulation of blood glucose and systemic acid-base balance through renal gluconeogenesis regulation.
Keywords: Acid-base homeostasis; Glucose metabolism; Ketone bodies; Renal gluconeogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










References
-
- Legouis D., Faivre A., Cippà P.E., de Seigneux S. Renal gluconeogenesis: an underestimated role of the kidney in systemic glucose metabolism. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022;37(8):1417–1425. - PubMed
-
- Gerich J.E., Meyer C., Woerle H.J., Stumvoll M. Renal gluconeogenesis: its importance in human glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Care. 2001;24(2):382–391. - PubMed
-
- Ekberg K., Landau B.R., Wajngot A., Chandramouli V., Efendic S., Brunengraber H., et al. Contributions by kidney and liver to glucose production in the postabsorptive state and after 60 h of fasting. Diabetes. 1999;48(2):292–298. - PubMed
-
- Meyer C., Dostou J.M., Welle S.L., Gerich J.E. Role of human liver, kidney, and skeletal muscle in postprandial glucose homeostasis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282(2):E419–E427. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

