Conceptual framework for establishing twins prevention and continuous health promotion programme: a qualitative study
- PMID: 38604635
- PMCID: PMC11015185
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080443
Conceptual framework for establishing twins prevention and continuous health promotion programme: a qualitative study
Abstract
Background: Twin registries and cohorts face numerous challenges, including significant resource allocation, twins' recruitment and retention. This study aimed to assess expert feedback on a proposed pragmatic idea for launching a continuous health promotion and prevention programme (HPPP) to establish and maintain twin cohorts.
Design: A qualitative study incorporating an inductive thematic analysis.
Setting: Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Participants: Researchers with expertise in twin studies participated in our study.
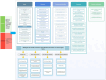
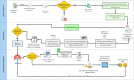
Analysis and design: Expert opinions were gathered through focus group discussions (FGDs). Thematic analysis was employed to analyse the findings and develop a model for designing a comprehensive, long-term health promotion programme using ATLAS.ti software. Additionally, a standardised framework was developed to represent the conceptual model of the twin HPPP.
Results: Eight FGDs were conducted, involving 16 experts. Thematic analysis identified eight themes and seven subthemes that encompassed the critical aspects of a continuous monitoring programme for twin health. Based on these identified themes, a conceptual framework was developed for the implementation of an HPPP tailored for twins.
Conclusion: This study presented the initial endeavour to establish a comprehensive and practical solution in the form of a continuous HPPP designed to tackle the obstacles of twins' cohorts.
Keywords: Health Services Accessibility; Health policy; PUBLIC HEALTH; Primary Health Care; QUALITATIVE RESEARCH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Nikolašević Ž, Dinić BM, Smederevac S, et al. Common genetic basis of the five factor model facets and intelligence: A twin study. Personality and Individual Differences 2021;175:110682. 10.1016/j.paid.2021.110682 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources