Conditional deficiency of Rho-associated kinases disrupts endothelial cell junctions and impairs respiratory function in adult mice
- PMID: 38604990
- PMCID: PMC11148122
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13802
Conditional deficiency of Rho-associated kinases disrupts endothelial cell junctions and impairs respiratory function in adult mice
Abstract
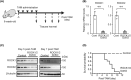
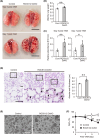
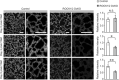
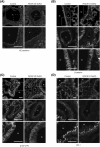
The Ras homology (Rho) family of GTPases serves various functions, including promotion of cell migration, adhesion, and transcription, through activation of effector molecule targets. One such pair of effectors, the Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases (ROCK1 and ROCK2), induce reorganization of actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesion through substrate phosphorylation. Studies on ROCK knockout mice have confirmed that ROCK proteins are essential for embryonic development, but their physiological functions in adult mice remain unknown. In this study, we aimed to examine the roles of ROCK1 and ROCK2 proteins in normal adult mice. Tamoxifen (TAM)-inducible ROCK1 and ROCK2 single and double knockout mice (ROCK1flox/flox and/or ROCK2flox/flox;Ubc-CreERT2) were generated and administered a 5-day course of TAM. No deaths occurred in either of the single knockout strains, whereas all of the ROCK1/ROCK2 double conditional knockout mice (DcKO) had died by Day 11 following the TAM course. DcKO mice exhibited increased lung tissue vascular permeability, thickening of alveolar walls, and a decrease in percutaneous oxygen saturation compared with noninducible ROCK1/ROCK2 double-floxed control mice. On Day 3 post-TAM, there was a decrease in phalloidin staining in the lungs in DcKO mice. On Day 5 post-TAM, immunohistochemical analysis also revealed reduced staining for vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin, β-catenin, and p120-catenin at cell-cell contact sites in vascular endothelial cells in DcKO mice. Additionally, VE-cadherin/β-catenin complexes were decreased in DcKO mice, indicating that ROCK proteins play a crucial role in maintaining lung function by regulating cell-cell adhesion.
Keywords: ROCK; actin cytoskeleton; cell–cell adhesion; lung function; transgenic mice; vascular permeability.
© 2024 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The CCM1-CCM2 complex controls complementary functions of ROCK1 and ROCK2 that are required for endothelial integrity.J Cell Sci. 2018 Aug 13;131(15):jcs216093. doi: 10.1242/jcs.216093. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30030370
-
The Rho Kinase Isoforms ROCK1 and ROCK2 Each Contribute to the Development of Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;58(4):471-481. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0075OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29211497 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the roles of ROCK isoforms in stress-induced cell detachment.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 15;12(10):1492-500. doi: 10.4161/cc.24699. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23598717 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
-
Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): structure, regulation, and functions.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29846. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29846. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25010901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blanchoin L, Boujemaa‐Paterski R, Sykes C and Plastino J (2014) Actin dynamics, architecture, and mechanics in cell motility. Physiol Rev 94, 235–263. - PubMed
-
- Heng YW and Koh CG (2010) Actin cytoskeleton dynamics and the cell division cycle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42, 1622–1633. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Peng L, Wang Z, Liu L, Cao M, Cui J, Wu F and Yang J (2023) Roles of the cytoskeleton in human diseases. Mol Biol Rep 50, 2847–2856. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

