Lymphatic vessels in the age of cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 38605228
- PMCID: PMC12312704
- DOI: 10.1038/s41568-024-00681-y
Lymphatic vessels in the age of cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
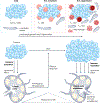
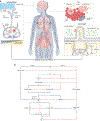
Lymphatic transport maintains homeostatic health and is necessary for immune surveillance, and yet lymphatic growth is often associated with solid tumour development and dissemination. Although tumour-associated lymphatic remodelling and growth were initially presumed to simply expand a passive route for regional metastasis, emerging research puts lymphatic vessels and their active transport at the interface of metastasis, tumour-associated inflammation and systemic immune surveillance. Here, we discuss active mechanisms through which lymphatic vessels shape their transport function to influence peripheral tissue immunity and the current understanding of how tumour-associated lymphatic vessels may both augment and disrupt antitumour immune surveillance. We end by looking forward to emerging areas of interest in the field of cancer immunotherapy in which lymphatic vessels and their transport function are likely key players: the formation of tertiary lymphoid structures, immune surveillance in the central nervous system, the microbiome, obesity and ageing. The lessons learnt support a working framework that defines the lymphatic system as a key determinant of both local and systemic inflammatory networks and thereby a crucial player in the response to cancer immunotherapy.
© 2024. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.W.L. reports consulting services for AGS Therapeutics. T.K. and T.M. declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Stacker SA et al. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodelling in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 159–172 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Leiter U et al. Final analysis of DeCOG-SLT trial: no survival benefit for complete lymph node dissection in patients with melanoma with positive sentinel node. J. Clin. Oncol. 37, 3000–3008 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

