METTL3 recruiting M2-type immunosuppressed macrophages by targeting m6A-SNAIL-CXCL2 axis to promote colorectal cancer pulmonary metastasis
- PMID: 38605400
- PMCID: PMC11007974
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03035-6
METTL3 recruiting M2-type immunosuppressed macrophages by targeting m6A-SNAIL-CXCL2 axis to promote colorectal cancer pulmonary metastasis
Abstract
Background: The regulatory role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in the onset and progression of cancer has garnered increasing attention in recent years. However, the specific role of m6A modification in pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer remains unclear.
Methods: This study identified differential m6A gene expression between primary colorectal cancer and its pulmonary metastases using transcriptome sequencing and immunohistochemistry. We investigated the biological function of METTL3 gene both in vitro and in vivo using assays such as CCK-8, colony formation, wound healing, EDU, transwell, and apoptosis, along with a BALB/c nude mouse model. The regulatory mechanisms of METTL3 in colorectal cancer pulmonary metastasis were studied using methods like methylated RNA immunoprecipitation quantitative reverse transcription PCR, RNA stability analysis, luciferase reporter gene assay, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR.
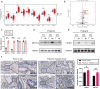
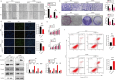
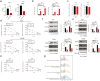
Results: The study revealed high expression of METTL3 and YTHDF1 in the tumors of patients with pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer. METTL3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer by m6A modification of SNAIL mRNA, where SNAIL enhances the secretion of CXCL2 through the NF-κB pathway. Additionally, colorectal cancer cells expressing METTL3 recruit M2-type macrophages by secreting CXCL2.
Conclusion: METTL3 facilitates pulmonary metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the m6A-Snail-CXCL2 axis to recruit M2-type immunosuppressive macrophages. This finding offers new research directions and potential therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer treatment.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer pulmonary metastases; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; M2-type macrophages; METTL3; N6-Methyladenosine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The regulatory role of m6A in cancer metastasis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 28;13:1539678. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1539678. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40356596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Oct 13;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1065-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31607270 Free PMC article.
-
SNAIL Induces EMT and Lung Metastasis of Tumours Secreting CXCL2 to Promote the Invasion of M2-Type Immunosuppressed Macrophages in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr 11;18(7):2867-2881. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66854. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541899 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO1 modification of methyltransferase-like 3 promotes tumor progression via regulating Snail mRNA homeostasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Theranostics. 2020 Apr 27;10(13):5671-5686. doi: 10.7150/thno.42539. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32483411 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification and post-translational modification of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 4;15(1):209. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01048-3. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38834851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role of m6A in cancer metastasis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 28;13:1539678. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1539678. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40356596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ_RUSC2 Sequesters miR-661 and Elevates TUSC2 Expression to Suppress Colorectal Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 24;26(7):2937. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072937. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243558 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Mar 26;20(1):20251167. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1167. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40177651 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine attenuates tumor-associated macrophages M2 polarization via suppressing the translation of Snail.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Aug 21. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2897-y. Online ahead of print. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40856928
-
RNA modifications in cancer immune therapy: regulators of immune cells and immune checkpoints.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1463847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1463847. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39372415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

