Mulberry branch fiber improved lipid metabolism and egg yolk fatty acid composition of laying hens via the enterohepatic axis
- PMID: 38605412
- PMCID: PMC11010431
- DOI: 10.1186/s40168-024-01788-y
Mulberry branch fiber improved lipid metabolism and egg yolk fatty acid composition of laying hens via the enterohepatic axis
Abstract
Background: The utilization of mulberry branch fiber (MF), the largest by-product of the sericulture industry, is an important issue. Supplementation with MF as a dietary fiber for poultry may serve as a useful application. However, little is known about the effects of MF on liver lipid metabolism and egg yolk fatty acid composition of laying hens and their underlying mechanisms. In this study, we performed a multi-omics investigation to explore the variations in liver lipid metabolism, egg yolk fatty acid composition, gut microbiota, and the associations among them induced by dietary MF in laying hens.
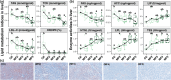
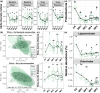
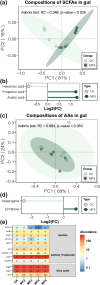
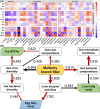
Results: Dietary MF had no harmful effects on the laying performance or egg quality in laying hens. The enzyme activities associated with lipid metabolism in the liver were altered by the addition of 5% MF, resulting in reduced liver fat accumulation. Furthermore, dietary 5% MF induced the variation in the fatty acid profiles of egg yolk, and increased the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content. We observed a significant reduction in the diversity of both gut bacteria and changes in their compositions after the addition of MF. Dietary MF significantly increased the abundance of genes involved in fatty acid biodegradation, and short-chain fatty acids biosynthesis in the gut microbiota of laying hens. The significant correlations were observed between the liver lipid metabolism enzyme activities of hepatic lipase, lipoprotein lipase, and total esterase with gut microbiota, including negative correlations with gut microbiota diversity, and multiple correlations with gut bacteria and viruses. Moreover, various correlations between the contents of PUFAs and monounsaturated fatty acids in egg yolk with the gut microbiota were obtained. Based on partial-least-squares path modeling integrated with the multi-omics datasets, we deduced the direct effects of liver enzyme activities and gut bacterial compositions on liver fat content and the roles of liver enzyme activities and gut bacterial diversity on egg yolk fatty acid composition.
Conclusions: The results indicate that dietary MF is beneficial to laying hens as it reduces the liver fat and improves egg yolk fatty acid composition through the enterohepatic axis. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Egg quality; Laying hen; Lipid metabolism; Multi-omics; Short-chain fatty acids.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of exogenous bile salts supplementation on the performance and hepatic lipid metabolism of aged laying hens.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad334. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad334. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37773415 Free PMC article.
-
Guanidinoacetic acid in laying hen diets with varying dietary energy: Productivity, antioxidant status, yolk fatty acid profile, hepatic lipid metabolism, and gut health.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105159. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105159. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40267570 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sumac (Rhus Coriaria L.) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) on egg yolk fatty acid, cholesterol and blood parameters in laying hens.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2017 Dec;101(6):1316-1323. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12652. Epub 2017 Feb 4. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28160334
-
A review of recent studies on the enrichment of eggs and poultry meat with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: novel findings and unanswered questions.Poult Sci. 2023 Oct;102(10):102938. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102938. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37572619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of the sex-linked dwarfing gene (dw) on the lipid composition of plasma, egg yolk and abdominal fat pad in White Leghorn laying hens: effect of dietary fat.J Nutr. 1989 Oct;119(10):1361-8. doi: 10.1093/jn/119.10.1361. J Nutr. 1989. PMID: 2685198 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of supplementation with vitamin D3 on growth performance, lipid metabolism and cecal microbiota in broiler chickens.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 6;12:1542637. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1542637. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 39981311 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenome-Assembled Genomes of Pig Fecal Samples in Nine European Countries: Insights into Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Viruses.Microorganisms. 2024 Nov 24;12(12):2409. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122409. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770612 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of microbiome and transcriptome reveals the mechanisms underlying the chlorogenic acid-mediated attenuation of oxidative stress and systemic inflammatory responses via gut-liver axis in post-peaking laying hens.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 6;16(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01216-7. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40474319 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of the bidirectional crosstalk between hepatic gene expressions and gut microbiota on the productive performances and egg quality of induced molting treated layer hens.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun;104(6):105135. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105135. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40203617 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine improves antioxidant capacity of chicken liver at high stocking density involved gut-liver microbiota axis based on multi-omics technologies.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):105015. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105015. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40106906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhong S, Li J, Chen X, Wen H. Research on the green total factor productivity of laying hens in China. J Clean Prod. 2021;315:128150. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128150. - DOI
-
- Lin H, De Vos D, Decuypere E, Buyse J. Dynamic changes in parameters of redox balance after mild heat stress in aged laying hens (Gallus gallus domesticus) Comp Biochem Phys C. 2008;147:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Jiang J, Qi L, Dai H, Hu C, Lv Z, Wei Q, et al. Dietary stevioside supplementation improves laying performance and eggshell quality through increasing estrogen synthesis, calcium level and antioxidant capacity of reproductive organs in aged breeder hens. Anim Feed Sci Tech. 2020;269:114682. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114682. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CARS-40-S25/China Agriculture Research System
- CARS-40-S25/China Agriculture Research System
- 2022YFD1601905/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2022YFD1601905/National Key R&D Program of China
- XDYC-CYCX-2022-0029/the Industrial Innovation Talent Project of the "Xing Dian Talent Support Program" of Yunnan Province in 2022
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

