Lessons From Prospective Longitudinal Follow-up of a French APECED Cohort
- PMID: 38605470
- PMCID: PMC11834711
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgae211
Lessons From Prospective Longitudinal Follow-up of a French APECED Cohort
Abstract
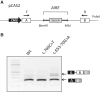
Background: Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy syndrome is a rare disease caused by biallelic mutations of the AIRE gene, usually presenting with the triad hypoparathyroidism-adrenal failure-chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC) and nonendocrine manifestations. The aim of this study was to determine the molecular profile of the AIRE gene, the prevalence of rare manifestations, and to characterize immunological disturbances in a French cohort.
Patients and methods: A national, multicenter prospective observational study to collect genetic, clinical, biological, and immunological data (NCT03751683).
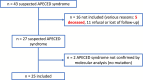
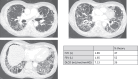
Results: Twenty-five patients (23 families) were enrolled. Eleven distinct AIRE variants were identified, 2 of which were not previously reported: an intronic variant, c.653-70G > A, and a c.1066del (p.Arg356GlyfsX22) variant (exon 9). The most common was the Finnish variant c.769C > T (16 alleles), followed by the variant c.967_979del13 (15 alleles), which seemed associated with a less severe phenotype. Seventeen out of 25 patients were homozygote. The median number of clinical manifestations was 7; 19/25 patients presented with the hypoparathyroidism-adrenal failure-CMC triad, 8/13 showed pulmonary involvement, 20/25 had ectodermal dystrophy, 8/25 had malabsorption, and 6/23 had asplenia. Fifteen out of 19 patients had natural killer cell lymphopenia with an increase in CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes and an age-dependent alteration of B lymphocyte homeostasis compared with matched controls (P < .001), related to the severity of the disease. All tested sera (n = 18) were positive for anti-interferon-α, 15/18 for anti-IL-22 antibodies, and 13/18 for anti-IL-17F antibodies, without clear phenotypic correlation other than with CMC.
Conclusion: This first prospective cohort showed a high AIRE genotype variability, with 2 new gene variants. The prevalence of potentially life-threatening nonendocrine manifestations was higher with systematic screening. These manifestations could, along with age-dependent B-cell lymphopenia, contribute to disease severity. Systematic screening for all the manifestations of the syndrome would allow earlier diagnosis, supporting vaccination and targeted therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: AIRE genotype; APECED syndrome; asplenia; autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1; pulmonary involvement.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Whitaker J, Landing BH, Esselborn VM, Williams RR. The syndrome of familial juvenile hypoadrenocorticism, hypoparathyroidism and superficial moniliasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956;16(10):1374‐1387. - PubMed
-
- Proust-Lemoine E, Saugier-Veber P, Wémeau JL. Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type I. Presse Médicale. 2012;41(12):e651‐e662. - PubMed
-
- Kisand K, Peterson P. Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy: known and novel aspects of the syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1246(1):77‐91. - PubMed
-
- Aaltonen J, Björses P, Sandkuijl L, Perheentupa J, Peltonen L. An autosomal locus causing autoimmune disease: autoimmune polyglandular disease type I assigned to chromosome 21. Nat Genet. 1994;8(1):83‐87. - PubMed
-
- Morimoto J, Matsumoto M, Miyazawa R, Yoshida H, Tsuneyama K, Matsumoto M. Aire suppresses CTLA-4 expression from the thymic stroma to control autoimmunity. Cell Rep. 2022;38(7):110384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

