Antitubercular drug-induced lichen planus: A case study with a mini literature review
- PMID: 38605770
- PMCID: PMC11006073
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_499_23
Antitubercular drug-induced lichen planus: A case study with a mini literature review
Abstract
Introduction: Drug-induced lichen planus is a cutaneous adverse effect that manifests as a systemic eruption of flat-topped, erythematous, or violaceous papules resembling lichen planus on the trunk and extremities. Although antitubercular therapy has been linked to cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions, the literature on such cases is scarce. Here, we present a case to contribute to this field, reporting on its presentation and management, and reviewing previous case studies.
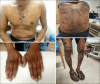
Case report: Our patient, a 63-year-old male, presented with black pigmented patches on the skin, having been diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and on antitubercular therapy for the past two months. A diagnosis of ATT-induced lichen planus was made, and all ATT was stopped. The patient was treated with antihistamines, apremilast, tacrolimus, and corticosteroids, and rechallenge of each drug was performed consecutively. No new lesions appeared after rechallenge with isoniazid and rifampicin. However, ethambutol was not reintroduced due to strong suspicion, by exclusion, that it was the offending agent, whereas on rechallenge with isoniazid and rifampicin, the patient's skin lesions gradually improved with eventual resolution of hyperpigmentation.
Discussion and conclusion: Lichenoid drug eruptions are characterized by type IV hypersensitivity reactions, and rechallenge is required to ensure safer treatment since the risk of disseminated and multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis increases with the cessation of antitubercular therapy.
Keywords: Antitubercular drugs; India; drug induced; lichenoid reaction; tuberculosis.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethambutol Induced Lichenoid Drug Eruption: A Case Report.Curr Drug Saf. 2021;16(3):296-298. doi: 10.2174/1574886315666201217095950. Curr Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33334297
-
[Lichenoid drug eruption with antituberculosis drugs associated with an anonychia].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Jun-Jul;147(6-7):456-460. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2019.09.618. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 32229034 French.
-
Spectrum of anti tubercular therapy induced cutaneous adverse drug reactions and its management through rechallenge: A prospective study at a Tertiary Care Centre.Indian J Tuberc. 2022 Oct;69(4):470-475. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2021.07.018. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Indian J Tuberc. 2022. PMID: 36460378
-
Lichen planus and other lichenoid dermatoses: Kids are not just little people.Clin Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;33(6):631-43. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 12. Clin Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26686015 Review.
-
Cutaneous lichenoid drug eruptions: A narrative review evaluating demographics, clinical features and culprit medications.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 May;37(5):965-975. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18879. Epub 2023 Feb 4. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. PMID: 36652271 Review.
Cited by
-
Patch Test-Positive Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms Syndrome Due to Cycloserine in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Case Report with a Review of the Literature.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025 Jan 7;112(4):854-855. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.24-0557. Print 2025 Apr 2. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025. PMID: 39773927 Review.
-
Drug-Induced Lichenoid Photosensitivity: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Apr 22;17(4):e82777. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82777. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40406781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pathave H, Dongre A, Gund G, Goutham S, Nayak C. A case series of generalized lichenoid drug eruption due to anti-tubercular drugs: Treated with immunosuppressant's while continuing anti-tubercular therapy. Indian J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;8:23–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijdd.ijdd_65_20.
-
- Singh P, Nathiya D, Jain S, Raj P, Suman S, Tomar BS. Case report isoniazid induced generalized lichenoid drug eruption: An unusual offender. Indian J Phar Pract. 2020;13:92–4. doi: https://doi.org/10.5530/ijopp. 13.3.x.
-
- Bhanja DB, Sil A, Panigrahi A, Chakraborty S. Rifampicin-induced lichenoid drug eruption. Postgrad Med J. 2020;96:782–3. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-137435. - PubMed
-
- Ali S. (2023, February). Isoniazid - induced lichenoid drug eruption presenting as exfoliative dermatitis in a South Asian woman- A case report. Open Journal of Clinical & Medical - jclinmedcasereports.com. https://jclinmedcasereports.com/articles/OJCMCR-1675.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous