Bounded rationality in healthcare: unraveling the psychological factors behind patient satisfaction in China
- PMID: 38605837
- PMCID: PMC11008602
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1296032
Bounded rationality in healthcare: unraveling the psychological factors behind patient satisfaction in China
Abstract
Introduction: Patient satisfaction is a crucial metric to gauge the quality of medical services, but the psychological factors influencing patient satisfaction remain insufficiently explored.
Methods: This study examines these psychological factors by applying the theory of bounded rationality to 1,442 inpatients in Hangzhou, China, whose data were collected using a questionnaire. One-way ANOVA, correlation analysis, and hierarchical regression were used to analyze patient satisfaction and its associated factors. Additionally, the path analysis of the structural equation model revealed the mechanisms behind the key psychological factors that influenced patient satisfaction.
Results: Medical risk perception, the social cognition of the medical environment, and social desirability bias had significant positive impacts on patient satisfaction. By contrast, negative emotions had a significant negative impact on patient satisfaction. Notably, patients' negative emotions had both a suppressive effect and a positive moderating effect on the relationship between medical risk perception and patient satisfaction. Similarly, social desirability bias had a suppressive effect on the correlation between the social cognition of the medical environment and patient satisfaction, albeit with a negative moderating effect.
Discussion: These results suggest that when evaluating and improving patient satisfaction, accounting only for the factors that directly influence medical service quality is insufficient, as the indirect and moderating effects of patients' negative emotions and the social cognition of the medical environment must also be considered. Medical service providers should thus address patients' negative emotions, establish good doctor-patient relationships, optimize service environments, provide managers with medical risk education and training on negative emotions, and prioritize patient-centered care. Additionally, the government and relevant health departments should optimize medical policies, enhance fairness and accessibility, and create a positive social cognitive environment through public education and awareness campaigns.
Keywords: bounded rationality theory; patient satisfaction; psychological factors; structural equation model; suppressive effect.
Copyright © 2024 Qian, Wang, Huang, Li, Jin, Chen and Sha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


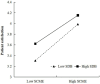
Similar articles
-
Social Context, Self-Efficacy, and Patient-Centered Service Behavior of Medical Professionals: The Moderating Role of Achievement Motivation.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 11;13:784228. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.784228. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35222112 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Medical Risk Perception on Patient Satisfaction: The Moderating Role of Shared Decision-Making.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Dec 4;17:2981-2995. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S482908. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 39649298 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between psychological health and social support: Evidence from physicians in China.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 29;15(1):e0228152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228152. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31995601 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of inpatient self-efficacy and trust in physicians on inpatient satisfaction with medical services: the mediating role of patient participation in medical decision-making.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1364319. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1364319. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39282672 Free PMC article.
-
Rationality, perception, and the all-seeing eye.Psychon Bull Rev. 2017 Aug;24(4):1040-1059. doi: 10.3758/s13423-016-1198-z. Psychon Bull Rev. 2017. PMID: 27928763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Rumman A., Al Shraah A., Al-Madi F., Alfalah T. (2022). The impact of quality framework application on patients’ satisfaction. Int. J. Hum. Rights Healthc. 15, 151–165. doi: 10.1108/IJHRH-01-2021-0006 - DOI
-
- Ajzen I. (2020). The theory of planned behavior: frequently asked questions. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2, 314–324. doi: 10.1002/hbe2.195 - DOI
-
- Alam S., Mahmud I., Hoque S. M. S., Akter R., Sohel Rana S. M. (2022). Predicting students’ intention to continue business courses on online platforms during the COVID-19: an extended expectation confirmation theory. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 20:100706. doi: 10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100706 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

