High frequencies of alpha common cold coronavirus/SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive functional CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells are associated with protection from symptomatic and fatal SARS-CoV-2 infections in unvaccinated COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 38605956
- PMCID: PMC11007208
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343716
High frequencies of alpha common cold coronavirus/SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive functional CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells are associated with protection from symptomatic and fatal SARS-CoV-2 infections in unvaccinated COVID-19 patients
Abstract
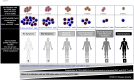
Background: Cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2-specific memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are present in up to 50% of unexposed, pre-pandemic, healthy individuals (UPPHIs). However, the characteristics of cross-reactive memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells associated with subsequent protection of asymptomatic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients (i.e., unvaccinated individuals who never develop any COVID-19 symptoms despite being infected with SARS-CoV-2) remains to be fully elucidated.
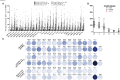
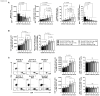
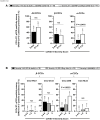
Methods: This study compares the antigen specificity, frequency, phenotype, and function of cross-reactive memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells between common cold coronaviruses (CCCs) and SARS-CoV-2. T-cell responses against genome-wide conserved epitopes were studied early in the disease course in a cohort of 147 unvaccinated COVID-19 patients who were divided into six groups based on the severity of their symptoms.
Results: Compared to severely ill COVID-19 patients and patients with fatal COVID-19 outcomes, the asymptomatic COVID-19 patients displayed significantly: (i) higher rates of co-infection with the 229E alpha species of CCCs (α-CCC-229E); (ii) higher frequencies of cross-reactive functional CD134+CD137+CD4+ and CD134+CD137+CD8+ T cells that cross-recognized conserved epitopes from α-CCCs and SARS-CoV-2 structural, non-structural, and accessory proteins; and (iii) lower frequencies of CCCs/SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive exhausted PD-1+TIM3+TIGIT+CTLA4+CD4+ and PD-1+TIM3+TIGIT+CTLA4+CD8+ T cells, detected both ex vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions: These findings (i) support a crucial role of functional, poly-antigenic α-CCCs/SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, induced following previous CCCs seasonal exposures, in protection against subsequent severe COVID-19 disease and (ii) provide critical insights into developing broadly protective, multi-antigen, CD4+, and CD8+ T-cell-based, universal pan-Coronavirus vaccines capable of conferring cross-species protection.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; CD4 + T cells; CD8 + T cells; COVID-19; asymptomatic; common cold coronavirus; exhaustion α-CCCs/SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells in asymptomatic COVID-19 infection; symptomatic.
Copyright © 2024 Coulon, Prakash, Dhanushkodi, Srivastava, Zayou, Tifrea, Edwards, Figueroa, Schubl, Hsieh, Nesburn, Kuppermann, Bahraoui, Vahed, Gil, Jones, Ulmer and BenMohamed.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors HV, DG, TJ and JU were employed by company TechImmune LLC. LB has an equity interest in TechImmune, LLC., a company that may potentially benefit from the research results and serves on the company’s Scientific Advisory Board. LB’s relationship with TechImmune, LLC., has been reviewed and approved by the University of California, Irvine by its conflict-of-interest policies. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Prakash S, Srivastava R, Coulon PG, Dhanushkodi NR, Chentoufi AA, Tifrea DF, et al. . Genome-wide B cell, CD4(+), and CD8(+) T cell epitopes that are highly conserved between human and animal coronaviruses, identified from SARS-CoV-2 as targets for preemptive pan-coronavirus vaccines. J Immunol. (2021) 206:2566–82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001438 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prakash S, Dhanushkodi NR, Zayou L, Ibraim IC, Quadiri A, Coulon PG, et al. . Cross-protection induced by highly conserved human B, CD4 (+,) and CD8 (+) T cell epitopes-based coronavirus vaccine against severe infection, disease, and death caused by multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Front Immunol. (2023) 15:1328905. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.24.541850 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahgat MM, Nadeem R, Nasraa MH, Amer K, Hassan WA, ELGarhy FM, et al. . Proinflammatory cytokine profiles in both mild symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2-infected Egyptian individuals and a proposed relationship to post-COVID-19 sequela. Viral Immunol. (2023) 36:600–9. doi: 10.1089/vim.2023.0060 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

