Motor properties of Myosin 5c are modulated by tropomyosin isoforms and inhibited by pentabromopseudilin
- PMID: 38606007
- PMCID: PMC11008601
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1394040
Motor properties of Myosin 5c are modulated by tropomyosin isoforms and inhibited by pentabromopseudilin
Abstract
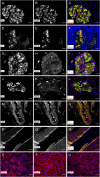
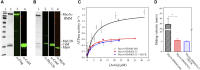
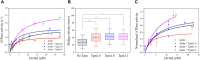
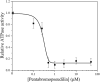
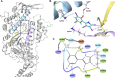
Myosin 5c (Myo5c) is a motor protein that is produced in epithelial and glandular tissues, where it plays an important role in secretory processes. Myo5c is composed of two heavy chains, each containing a generic motor domain, an elongated neck domain consisting of a single α-helix with six IQ motifs, each of which binds to a calmodulin (CaM) or a myosin light chain from the EF-hand protein family, a coiled-coil dimer-forming region and a carboxyl-terminal globular tail domain. Although Myo5c is a low duty cycle motor, when two or more Myo5c-heavy meromyosin (HMM) molecules are linked together, they move processively along actin filaments. We describe the purification and functional characterization of human Myo5c-HMM co-produced either with CaM alone or with CaM and the essential and regulatory light chains Myl6 and Myl12b. We describe the extent to which cofilaments of actin and Tpm1.6, Tpm1.8 or Tpm3.1 alter the maximum actin-activated ATPase and motile activity of the recombinant Myo5c constructs. The small allosteric effector pentabromopseudilin (PBP), which is predicted to bind in a groove close to the actin and nucleotide binding site with a calculated ΔG of -18.44 kcal/mol, inhibits the motor function of Myo5c with a half-maximal concentration of 280 nM. Using immunohistochemical staining, we determined the distribution and exact localization of Myo5c in endothelial and endocrine cells from rat and human tissue. Particular high levels of Myo5c were observed in insulin-producing β-cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans.
Keywords: Myosin 5c; immunohistochemistry; molecular docking; pentabromopseudilin; tropomyosin.
Copyright © 2024 Kengyel, Palarz, Krohn, Marquardt, Greve, Heiringhoff, Jörns and Manstein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

