Repeat hepatectomy versus thermal ablation therapy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38606103
- PMCID: PMC11007030
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1370390
Repeat hepatectomy versus thermal ablation therapy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This meta-analysis was conducted to assess the survival benefits of repeat hepatectomy (RH) and thermal ablation therapy (TAT) in managing recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
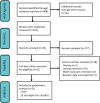
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in the PubMed, SinoMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Medline, and Web of Science databases using relevant keywords to identify all studies published on this specific topic. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using a fixed-effects model.
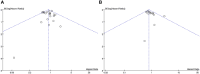
Results: This meta-analysis included a total of 21 studies, comprising 2580 patients with recurrent HCC, among whom 1189 underwent RH and 1394 underwent TAT. Meta-analysis results demonstrated that the RH group exhibited superior overall survival (OS) (HR=0.85, 95%CI 0.76∼0.95, P=0.004) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (HR=0.79, 95%CI 0.7∼0.9, P<0.01) compared to the TAT group. Regarding postoperative complications, the TAT group experienced fewer complications than the RH group (OR=3.23, 95%CI 1.48∼7.07, P=0.003), while no significant difference in perioperative mortality was observed between the two groups (OR=2.11, 95%CI 0.54∼8.19, P=0.28).
Conclusion: The present study demonstrates that, in comparison to TAT, RH may confer superior survival benefits for patients with recurrent HCC.
Keywords: meta-analysis; recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma; repeat hepatectomy; systematic review; thermal ablation therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Dong, Zhang, Wan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of repeat hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a Systematic Review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 26;15:1559491. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1559491. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40206586 Free PMC article.
-
Repeat hepatectomy versus microwave ablation for solitary and small (≤3 cm) recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with early or late recurrence: A propensity score matched study.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023 May;49(5):1001-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.12.016. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36585301
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of repeated hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of primary recurrent liver cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jun 6;20(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02649-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35668464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 27;20(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01544-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33246417 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of survival and post-operation outcomes for minimally invasive versus open hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case-matched studies.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 20;12:1021804. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1021804. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36338679 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

