Case report: Efficacy of icotinib treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a rare case of double primary malignant tumors
- PMID: 38606154
- PMCID: PMC11006962
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1266062
Case report: Efficacy of icotinib treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a rare case of double primary malignant tumors
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is rare and the prognosis is poor, therefore there is an urgent need to improve this situation. The objective of this study was to explore the effect of first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in the patient of the double primary malignant tumors.
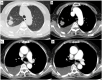
Case report: We report a case of lung adenocarcinoma with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated by icotininb after five-year follow-up. A 71-year-old Chinese woman complaining of swallowing obstruction, heartburn, regurgitation of gastric acid for more than 2 months. An esophageal lesion was found by chest CT scans in T7 vertebral level. The diagnosis by gastroscopic biopsy was squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) with EGFR over-expression. Simultaneously, chest CT showed a 2 cm x 1 cm solitary lesion in the right superior pulmonary. The histological diagnosis by percutaneous lung Biopsy was "adenocarcinoma." Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutation status was evaluated by Sanger sequencing, and an exon 21 point mutation (L858R) was identified. When the double primary malignant tumors were diagnosed, the patient refused operation and received a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), icotinib, at the dose of 125 mg, three times per day. All serum tumor biomarkers such as CEA and cancer antigen 125 (CA125) were in the normal range during the treatment period. After five-year follow-up, the patient has no evidence of recurrence or metastasis. The lung cancer was stable, meanwhile the esophageal lesion was almost cured.
Conclusion: Icotininb is an effective treatment in the patients of the double primary malignant tumors of lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR gene mutation and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with EGFR over-expression.
Keywords: double primary malignant tumors; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; icotinib; lung adenocarcinoma; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024 Deng, Li, Mu, Wei and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Afatinib overcoming resistance to icotinib and osimertinib in NSCLC with leptomeningeal metastasis in patients with acquired EGFR L858R/T790M or L858R/S768I mutations: Two case reports.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 8;9(10):e20690. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20690. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37860534 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of Switching EGFR-TKIs for Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Due to Interstitial Lung Disease: A Case Report.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024 Jul 5. doi: 10.2174/0115680096313868240603090903. Online ahead of print. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38982693
-
Efficacy of icotinib in advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2018 Sep;7(9):4456-4466. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1736. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30109777 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Osimertinib in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with EGFR Gene Mutation-Case Report and a Literature Review.Curr Oncol. 2022 May 13;29(5):3531-3539. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29050285. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35621675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome of EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma NSCLC patients with changed phenotype to squamous cell carcinoma after tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A pooled analysis with an additional case.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jan;127:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30642539 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

