IgG4-Related Membranous Nephropathy After COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report
- PMID: 38606210
- PMCID: PMC11008612
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.56028
IgG4-Related Membranous Nephropathy After COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report
Abstract
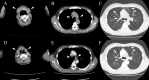
Although immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related kidney diseases are typically characterized by tubulointerstitial nephritis with abundant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells and fibrosis, there have been relatively rare cases of IgG4-related glomerulonephritis. Several cases of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccination have been reported. However, there are no reports of IgG4-related glomerulonephritis following COVID-19 vaccination. Herein, we present a case of IgG4-related membranous nephropathy (MN) occurring after COVID-19 vaccination. A 69-year-old Japanese male presented to our hospital with edema that started the day after his second COVID-19 vaccination. The patient exhibited nephrotic syndrome and was diagnosed with MN based on the results of a kidney biopsy. Although serum IgG4 levels were elevated to 946 mg/dL, no evidence of organ involvement suggestive of IgG4-RD was observed. Treatment with prednisolone and cyclosporine resulted in complete remission, and immunosuppressive agents were tapered. However, one month after discontinuing the immunosuppressive agents, the patient was readmitted with swelling around the submandibular glands and exertional dyspnea. Serum IgG4 level was markedly elevated at 2,320 mg/dL, and computed tomography revealed submandibular gland swelling and thickening of the interlobular septum and bronchovascular bundles in both lungs. The patient was diagnosed with IgG4-RD based on elevated serum IgG4 levels and infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the submandibular gland biopsy. Upon resuming treatment with prednisolone, the symptoms attributed to IgG4-RD improved within a few days. In cases of nephrotic syndrome following COVID-19 vaccination, it may be advisable to conduct detailed examinations to assess the possibility of the development of IgG4-RDs.
Keywords: covid-19 vaccine; igg4-related disease; igg4-related kidney disease; membranous glomerulopathy; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2024, Mizuno et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
IgG4-Related Membranous Nephropathy with Acute Nephrotic Syndrome During Successful Steroid Maintenance Treatment for Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis.Am J Case Rep. 2023 Aug 18;24:e940707. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.940707. Am J Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37592742 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) with membranous nephropathy as its initial manifestation: report of one case and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1419-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31311519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG4-related disease involving vital organs diagnosed with lip biopsy: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(24):e3970. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003970. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27311008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-density lipoprotein apheresis for PLA2R-related membranous glomerulonephritis accompanied by IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis.CEN Case Rep. 2020 Nov;9(4):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00494-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. CEN Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32557252 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological Patterns and Predictors of the Functional Restoration of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Kidney Disease: A Chinese Single-Center Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 6;8:736098. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.736098. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34692728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31:529–533. - PubMed
-
- A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–984. - PubMed
-
- New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination. Chen Y, Xu Z, Wang P, Li XM, Shuai ZW, Ye DQ, Pan HF. Immunology. 2022;165:386–401. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
