Me31B: a key repressor in germline regulation and beyond
- PMID: 38606619
- PMCID: PMC11065648
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20231769
Me31B: a key repressor in germline regulation and beyond
Abstract
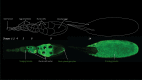
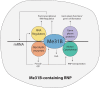
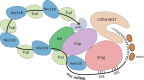
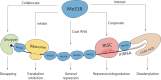
Maternally Expressed at 31B (Me31B), an evolutionarily conserved ATP-dependent RNA helicase, plays an important role in the development of the germline across diverse animal species. Its cellular functionality has been posited as a translational repressor, participating in various RNA metabolism pathways to intricately regulate the spatiotemporal expression of RNAs. Despite its evident significance, the precise role and mechanistic underpinnings of Me31B remain insufficiently understood. This article endeavors to comprehensively review historic and recent research on Me31B, distill the major findings, discern generalizable patterns in Me31B's functions across different research contexts, and provide insights into its fundamental role and mechanism of action. The primary focus of this article centers on elucidating the role of Drosophila Me31B within the germline, while concurrently delving into pertinent research on its orthologs within other species and cellular systems.
Keywords: Germ granules; Germline; Me31B; Neuronal granules; RNA helicase; Ribonucleoprotein (RNP).
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Proteomics Reveal Me31B's Interactome Dynamics, Expression Regulation, and Assembly Mechanism into Germ Granules during Drosophila Germline Development.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 17;10(1):564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57492-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31953495 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of the functional motifs of the DEAD-box RNA helicase Me31B/DDX6 in Drosophila germline development.FEBS Lett. 2023 Jul;597(14):1848-1867. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14668. Epub 2023 Jun 8. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 37235728 Free PMC article.
-
An in vivo proteomic analysis of the Me31B interactome in Drosophila germ granules.FEBS Lett. 2017 Nov;591(21):3536-3547. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12854. Epub 2017 Oct 11. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28945271
-
Next generation organelles: structure and role of germ granules in the germline.Mol Reprod Dev. 2013 Aug;80(8):610-23. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22115. Epub 2012 Nov 13. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23011946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germ granules in Drosophila.Traffic. 2019 Sep;20(9):650-660. doi: 10.1111/tra.12674. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 31218815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclin A and B mRNAs by Bruno 1, Cup, and P-bodies.iScience. 2025 May 21;28(6):112727. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112727. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40546942 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclin A and cyclin B mRNAs is mediated by Bruno 1 and Cup, and further fine-tuned within P-bodies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 21:2024.10.17.618951. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.17.618951. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: iScience. 2025 May 21;28(6):112727. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112727. PMID: 39464095 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Characterization of transcriptomics during aging and genes required for lifespan in Drosophila intestine.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 26;15(1):14692. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98888-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40287511 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila and human Headcase define a new family of ribonucleotide granule proteins required for stress response.Sci Adv. 2025 Mar 28;11(13):eads2086. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads2086. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40153502 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

