Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals unique Hsp90 cycle-dependent client interactions
- PMID: 38606935
- PMCID: PMC11151932
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyae057
Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals unique Hsp90 cycle-dependent client interactions
Abstract
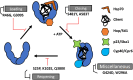
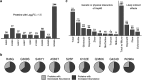
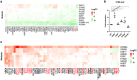
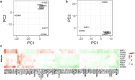
Hsp90 is an abundant and essential molecular chaperone that mediates the folding and activation of client proteins in a nucleotide-dependent cycle. Hsp90 inhibition directly or indirectly impacts the function of 10-15% of all proteins due to degradation of client proteins or indirect downstream effects. Due to its role in chaperoning oncogenic proteins, Hsp90 is an important drug target. However, compounds that occupy the ATP-binding pocket and broadly inhibit function have not achieved widespread use due to negative effects. More selective inhibitors are needed; however, it is unclear how to achieve selective inhibition. We conducted a quantitative proteomic analysis of soluble proteins in yeast strains expressing wild-type Hsp90 or mutants that disrupt different steps in the client folding pathway. Out of 2,482 proteins in our sample set (approximately 38% of yeast proteins), we observed statistically significant changes in abundance of 350 (14%) of those proteins (log2 fold change ≥ 1.5). Of these, 257/350 (∼73%) with the strongest differences in abundance were previously connected to Hsp90 function. Principal component analysis of the entire dataset revealed that the effects of the mutants could be separated into 3 primary clusters. As evidence that Hsp90 mutants affect different pools of clients, simultaneous co-expression of 2 mutants in different clusters restored wild-type growth. Our data suggest that the ability of Hsp90 to sample a wide range of conformations allows the chaperone to mediate folding of a broad array of clients and that disruption of conformational flexibility results in client defects dependent on those states.
Keywords: DIA-MS; client-specific effects; cochaperone; molecular chaperone.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest. The author(s) declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disrupting progression of the yeast Hsp90 folding pathway at different transition points results in client-specific maturation defects.Genetics. 2021 Mar 31;217(3):iyab009. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab009. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33789348 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 mutants with distinct defects provide novel insights into cochaperone regulation of the folding cycle.PLoS Genet. 2023 May 25;19(5):e1010772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010772. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37228112 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide-dependent interaction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp90 with the cochaperone proteins Sti1, Cpr6, and Sba1.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jan;27(2):768-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01034-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17101799 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Hsp90 mechanism and in vivo functions learned from studies in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 8;11:1325590. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1325590. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38389899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular interaction network of the Hsp90 chaperone system.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;594:27-36. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-39975-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17205672 Review.
Cited by
-
Hsp90 and cochaperones have two genetically distinct roles in regulating eEF2 function.PLoS Genet. 2024 Dec 9;20(12):e1011508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011508. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39652595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An WG, Schulte TW, Neckers LM. 2000. The heat shock protein 90 antagonist geldanamycin alters chaperone association with p210bcr-abl and v-src proteins before their degradation by the proteasome. Cell Growth Differ. 11:355–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

