Gene Delivery and Analysis of Optogenetic Induction of Lytic Cell Death
- PMID: 38606936
- PMCID: PMC11163966
- DOI: 10.1002/cpz1.1023
Gene Delivery and Analysis of Optogenetic Induction of Lytic Cell Death
Abstract
Necroptosis is a form of inflammatory lytic cell death involving active cytokine production and plasma membrane rupture. Progression of necroptosis is tightly regulated in time and space, and its signaling outcomes can shape the local inflammatory environment of cells and tissues. Pharmacological induction of necroptosis is well established, but the diffusive nature of chemical death inducers makes it challenging to study cell-cell communication precisely during necroptosis. Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3, or RIPK3, is a crucial signaling component of necroptosis, acting as a crucial signaling node for both canonical and non-canonical necroptosis. RIPK3 oligomerization is crucial to the formation of the necrosome, which regulates plasma membrane rupture and cytokine production. Commonly used necroptosis inducers can activate multiple downstream signaling pathways, confounding the signaling outcomes of RIPK3-mediated necroptosis. Opsin-free optogenetic techniques may provide an alternative strategy to address this issue. Optogenetics uses light-sensitive protein-protein interaction to modulate cell signaling. Compared to chemical-based approaches, optogenetic strategies allow for spatiotemporal modulation of signal transduction in live cells and animals. We developed an optogenetic system that allows for ligand-free optical control of RIPK3 oligomerization and necroptosis. This article describes the sample preparation, experimental setup, and optimization required to achieve robust optogenetic induction of RIPK3-mediated necroptosis in colorectal HT-29 cells. We expect that this optogenetic system could provide valuable insights into the dynamic nature of lytic cell death. © 2024 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Production of lentivirus encoding the optogenetic RIPK3 system Support Protocol: Quantification of the titer of lentivirus Basic Protocol 2: Culturing, chemical transfection, and lentivirus transduction of HT-29 cells Basic Protocol 3: Optimization of optogenetic stimulation conditions Basic Protocol 4: Time-stamped live-cell imaging of HT-29 lytic cell death Basic Protocol 5: Quantification of HT-29 lytic cell death.
Keywords: RIPK3; cell signaling; lytic cell death; necroptosis; optogenetic.
© 2024 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT:
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
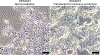
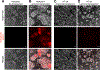
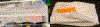


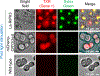
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

