CD99 Expression and Prognostic Impact in Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Cohort Study
- PMID: 38607036
- PMCID: PMC11012029
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13070597
CD99 Expression and Prognostic Impact in Glioblastoma: A Single-Center Cohort Study
Abstract
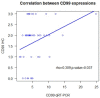
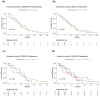
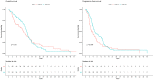
Glioblastoma is the most frequent and aggressive brain tumor in adults. This study aims to evaluate the expression and prognostic impact of CD99, a membrane glycoprotein involved in cellular migration and invasion. In a cohort of patients with glioblastoma treated with surgery, radiotherapy and temozolomide, we retrospectively analyzed tumor expression of CD99 by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) for both the wild type (CD99wt) and the truncated (CD99sh) isoforms. The impact on overall survival (OS) was assessed with the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test and by multivariable Cox regression. Forty-six patients with glioblastoma entered this study. Immunohistochemical expression of CD99 was present in 83%. Only the CD99wt isoform was detected by qRT-PCR and was significantly correlated with CD99 expression evaluated by IHC (rho = 0.309, p = 0.037). CD99 expression was not associated with OS, regardless of the assessment methodology used (p = 0.61 for qRT-PCR and p = 0.73 for IHC). In an exploratory analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas, casuistry of glioblastomas CD99 expression was not associated with OS nor with progression-free survival. This study confirms a high expression of CD99 in glioblastoma but does not show any significant impact on survival. Further preclinical studies are needed to define its role as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.
Keywords: CD99; glioblastoma; immunohistochemistry; prognostic factor; quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
V.F. and T.D.M. are employees of Diatheva srl. The other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma in the elderly: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 23;3(3):CD013261. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013261.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32202316 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD99: A Key Regulator in Immune Response and Tumor Microenvironment.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 28;15(5):632. doi: 10.3390/biom15050632. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD99 is a potential diagnostic and immunological biomarker in pan-cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 18;16(1):1574. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03419-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40824501
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

