The Role of Semaphorins in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 38607057
- PMCID: PMC11011349
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13070618
The Role of Semaphorins in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
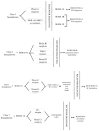
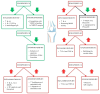
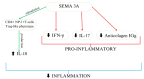
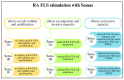
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases. Inflammation of the synovial fluid propagates the pathological process of angiogenesis. Semaphorins play a crucial role in the context of endothelial cell function, and their pleiotropic nature has various effects on the further development of RA. This narrative review summarises the various roles of semaphorins in the pathology of RA and whether they could play a role in developing novel RA treatment options.
Keywords: angiogenesis; rheumatoid arthritis; semaphorins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Semaphorins: From Angiogenesis to Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Sep;73(9):1579-1588. doi: 10.1002/art.41701. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33605067
-
Semaphorin 4D Contributes to Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inducing Inflammatory Cytokine Production: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;67(6):1481-90. doi: 10.1002/art.39086. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25707877 Free PMC article.
-
The role of semaphorins in immune responses and autoimmune rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Jan;14(1):19-31. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.201. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29213125 Review.
-
[Semaphorins as treatment targets for cartilage and bone damage caused by rheumatoid arthritis].Clin Calcium. 2015 Dec;25(12):1795-800. Clin Calcium. 2015. PMID: 26608854 Japanese.
-
Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2069-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602936 Review.
Cited by
-
Trichinella spiralis Paramyosin Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Modulating CD4+ T Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 18;25(12):6706. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126706. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928413 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Advances in Molecular Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis: From In Vitro to Clinic Applications Using Radiolabeled Targeting Vectors with Technetium-99m.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(6):751. doi: 10.3390/life14060751. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation analysis of circulating PCDH17 DNA methylation changes with rheumatoid arthritis patients.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):17939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02236-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410297 Free PMC article.
-
DNA and RNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Narrative Review.Epigenomes. 2025 Jan 8;9(1):2. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes9010002. Epigenomes. 2025. PMID: 39846569 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

