From Vessels to Neurons-The Role of Hypoxia Pathway Proteins in Embryonic Neurogenesis
- PMID: 38607059
- PMCID: PMC11012138
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13070621
From Vessels to Neurons-The Role of Hypoxia Pathway Proteins in Embryonic Neurogenesis
Abstract
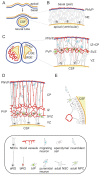
Embryonic neurogenesis can be defined as a period of prenatal development during which divisions of neural stem and progenitor cells give rise to neurons. In the central nervous system of most mammals, including humans, the majority of neocortical neurogenesis occurs before birth. It is a highly spatiotemporally organized process whose perturbations lead to cortical malformations and dysfunctions underlying neurological and psychiatric pathologies, and in which oxygen availability plays a critical role. In case of deprived oxygen conditions, known as hypoxia, the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) signaling pathway is activated, resulting in the selective expression of a group of genes that regulate homeostatic adaptations, including cell differentiation and survival, metabolism and angiogenesis. While a physiological degree of hypoxia is essential for proper brain development, imbalanced oxygen levels can adversely affect this process, as observed in common obstetrical pathologies such as prematurity. This review comprehensively explores and discusses the current body of knowledge regarding the role of hypoxia and the HIF pathway in embryonic neurogenesis of the mammalian cortex. Additionally, it highlights existing gaps in our understanding, presents unanswered questions, and provides avenues for future research.
Keywords: HIF; NSC; embryonic neurogenesis; hypoxia; neocortex; neural progenitor cells; vascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hes5 regulates the transition timing of neurogenesis and gliogenesis in mammalian neocortical development.Development. 2017 Sep 1;144(17):3156-3167. doi: 10.1242/dev.147256. Development. 2017. PMID: 28851724
-
Sonic hedgehog and notch signaling can cooperate to regulate neurogenic divisions of neocortical progenitors.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 17;6(2):e14680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014680. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21379383 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Immunoreactivity of Pax6 in the Neurogenic Zone After Chronic Prenatal Hypoxia.In Vivo. 2017 Nov-Dec;31(6):1125-1129. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11178. In Vivo. 2017. PMID: 29102934 Free PMC article.
-
How neural stem cells contribute to neocortex development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Nov 1;49(5):1997-2006. doi: 10.1042/BST20200923. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34397081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into the Role of Mild Hypoxia in Regulating Neural Stem Cell Characteristics.Stem Cells Dev. 2024 Jul;33(13-14):333-342. doi: 10.1089/scd.2024.0020. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Stem Cells Dev. 2024. PMID: 38753713 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling Neurodevelopment: Synergistic Effects of Intrinsic Genetic Programs and Extrinsic Environmental Cues.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(22):e2414890. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414890. Epub 2025 May 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40323170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial Cell Reprogramming in Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Recent Advancements and Translational Challenges.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Feb 4. doi: 10.1007/s12975-025-01331-7. Online ahead of print. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39904845 Review.
-
Oxygen Saturation Targeting in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 4;14(11):3975. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113975. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sanides F. Comparative Architectonics of the Neocortex Of Mammals snd Their Evolutionary Interpretation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1969;167:404–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb20459.x. - DOI
-
- Striedter G.F. Principles of Brain Evolution. Sinauer Associates Inc.; Sunderland, MA, USA: 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

