Enrichment, Characterization, and Proteomic Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Limbal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Melanocytes
- PMID: 38607062
- PMCID: PMC11011788
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13070623
Enrichment, Characterization, and Proteomic Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Limbal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Melanocytes
Abstract
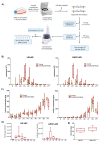
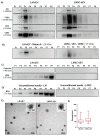
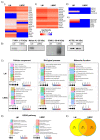
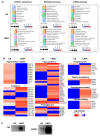
Limbal epithelial progenitor cells (LEPC) rely on their niche environment for proper functionality and self-renewal. While extracellular vesicles (EV), specifically small EVs (sEV), have been proposed to support LEPC homeostasis, data on sEV derived from limbal niche cells like limbal mesenchymal stromal cells (LMSC) remain limited, and there are no studies on sEVs from limbal melanocytes (LM). In this study, we isolated sEV from conditioned media of LMSC and LM using a combination of tangential flow filtration and size exclusion chromatography and characterized them by nanoparticle tracking analysis, transmission electron microscopy, Western blot, multiplex bead arrays, and quantitative mass spectrometry. The internalization of sEV by LEPC was studied using flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. The isolated sEVs exhibited typical EV characteristics, including cell-specific markers such as CD90 for LMSC-sEV and Melan-A for LM-sEV. Bioinformatics analysis of the proteomic data suggested a significant role of sEVs in extracellular matrix deposition, with LMSC-derived sEV containing proteins involved in collagen remodeling and cell matrix adhesion, whereas LM-sEV proteins were implicated in other cellular bioprocesses such as cellular pigmentation and development. Moreover, fluorescently labeled LMSC-sEV and LM-sEV were taken up by LEPC and localized to their perinuclear compartment. These findings provide valuable insights into the complex role of sEV from niche cells in regulating the human limbal stem cell niche.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; limbal epithelial progenitor cells; limbal melanocytes; limbal mesenchymal stromal cells; limbal stem cell niche; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteomic Insights into Human Limbal Epithelial Progenitor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 Jun;21(5):1578-1593. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10877-w. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40238075 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Isolation and Functional Characterization of Niche Cells from Human Corneal Limbus.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2750. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052750. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269891 Free PMC article.
-
P-Cadherin Is Expressed by Epithelial Progenitor Cells and Melanocytes in the Human Corneal Limbus.Cells. 2022 Jun 20;11(12):1975. doi: 10.3390/cells11121975. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741104 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics analysis of circulating small extracellular vesicles: Focus on the contribution of EVs to tumor metabolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023 Oct;73:3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.08.003. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023. PMID: 37652834 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Dec 21;18:100522. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100522. eCollection 2023 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36593913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes as Future Therapeutic Tools and Targets for Corneal Diseases.Cells. 2025 Jun 23;14(13):959. doi: 10.3390/cells14130959. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in Ocular Health: Recent Insights into Pathology, Diagnostic Applications and Therapeutic Functions.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 19;13(1):233. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010233. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Types Exhibit Distinctive Surface Protein Profiling and Molecular Characteristics: A Comparative Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 4;26(7):3393. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073393. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244251 Free PMC article.
-
PAX3 expression patterns in ocular surface melanocytes.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 11;15(1):12472. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90318-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40216818 Free PMC article.
-
The lincRNA Pantr1 is a FOXG1 target gene conferring site-specific chromatin binding of FOXG1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 20;53(12):gkaf539. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf539. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40548942 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

