Current Advances of Nanomaterial-Based Oral Drug Delivery for Colorectal Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 38607092
- PMCID: PMC11013305
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14070557
Current Advances of Nanomaterial-Based Oral Drug Delivery for Colorectal Cancer Treatment
Abstract
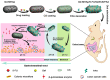
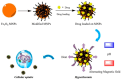
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a common malignant tumor, and traditional treatments include surgical resection and radiotherapy. However, local recurrence, distal metastasis, and intestinal obstruction are significant problems. Oral nano-formulation is a promising treatment strategy for CRC. This study introduces physiological and environmental factors, the main challenges of CRC treatment, and the need for a novel oral colon-targeted drug delivery system (OCDDS). This study reviews the research progress of controlled-release, responsive, magnetic, targeted, and other oral nano-formulations in the direction of CRC treatment, in addition to the advantages of oral colon-targeted nano-formulations and concerns about the oral delivery of related therapeutic agents to inspire related research.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; nano-drug delivery system; oral; oral colon-targeted drug delivery system (OCDDS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mitochondria-targeting folic acid-modified nanoplatform based on mesoporous carbon and a bioactive peptide for improved colorectal cancer treatment.Acta Biomater. 2022 Oct 15;152:453-472. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.08.071. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36084923
-
Oral delivery of micro/nanoparticulate systems based on natural polysaccharides for intestinal diseases therapy: Challenges, advances and future perspectives.J Control Release. 2021 Jun 10;334:353-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.04.026. Epub 2021 Apr 24. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33901582 Review.
-
Targeted and intelligent nano-drug delivery systems for colorectal cancer treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 25;13:1582659. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1582659. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40352359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-Drug Delivery Systems Based on Different Targeting Mechanisms in the Targeted Therapy of Colorectal Cancer.Molecules. 2022 May 6;27(9):2981. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092981. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies of targeting oral drug delivery systems to the colon and their potential use for the treatment of colorectal cancer.Pharm Dev Technol. 2012 Sep-Oct;17(5):521-40. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2012.696268. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Pharm Dev Technol. 2012. PMID: 22681390 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoformulations in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications: Green Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 27;25(11):5842. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115842. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbiotics: Modulation of the Gut Microbiota and Potential for Association with Nanotechnology.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jul 18. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10675-3. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40679568 Review.
-
Mapping the intellectual structure and emerging trends on nanomaterials in colorectal cancer: a bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2024.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 8;14:1514581. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1514581. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39845318 Free PMC article.
-
Transformative Impact of Nanocarrier-Mediated Drug Delivery: Overcoming Biological Barriers and Expanding Therapeutic Horizons.Small Sci. 2024 Sep 17;4(11):2400280. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400280. eCollection 2024 Nov. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40213439 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured Formulations for a Local Treatment of Cancer: A Mini Review About Challenges and Possibilities.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 6;17(2):205. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020205. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu B., Jiang G., Yu W., Liu D., Liu Y., Kong X., Yao J. Preparation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and chitosan composite nanocarriers via electrostatic self assembly for oral delivery of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017;78:420–428. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.04.113. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

