In-Membrane Enrichment and Peptic Digestion to Facilitate Analysis of Monoclonal Antibody Glycosylation
- PMID: 38607313
- PMCID: PMC11283323
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c00030
In-Membrane Enrichment and Peptic Digestion to Facilitate Analysis of Monoclonal Antibody Glycosylation
Abstract
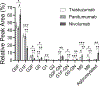
The number of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is growing rapidly due to their widespread use for treating various diseases and health conditions. Assessing the glycosylation profile of mAbs during production is essential to ensuring their safety and efficacy. This research aims to rapidly isolate and digest mAbs for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) identification of glycans and monitoring of glycosylation patterns, potentially during manufacturing. Immobilization of an Fc region-specific ligand, oFc20, in a porous membrane enables the enrichment of mAbs from cell culture supernatant and efficient elution with an acidic solution. Subsequent digestion of the mAb eluate occurred in a pepsin-modified membrane within 5 min. The procedure does not require alkylation and desalting, greatly shortening the sample preparation time. Subsequent LC-MS/MS analysis identified 11 major mAb N-glycan proteoforms and assessed the relative peak areas of the glycosylated peptides. This approach is suitable for the glycosylation profiling of various human IgG mAbs, including biosimilars and different IgG subclasses. The total time required for this workflow is less than 2 h, whereas the conventional enzymatic release and labeling of glycans can take much longer. Thus, the integrated membranes are suitable for facilitating the analysis of mAb glycosylation patterns.
Figures

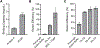

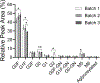

Similar articles
-
Comparison of methods for the analysis of therapeutic immunoglobulin G Fc-glycosylation profiles-Part 2: Mass spectrometric methods.MAbs. 2015;7(4):732-42. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1045173. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25996192 Free PMC article.
-
Pepsin-Containing Membranes for Controlled Monoclonal Antibody Digestion Prior to Mass Spectrometry Analysis.Anal Chem. 2015 Nov 3;87(21):10942-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02739. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26455365 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS peptide mapping with automated data processing for routine profiling of N-glycans in immunoglobulins.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 Jun;25(6):999-1011. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0858-3. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 24664809
-
Characterization of Pharmaceutical IgG and Biosimilars Using Miniaturized Platforms and LC-MS/MS.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(9):788-801. doi: 10.2174/1389201017666160401145012. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27033511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation of biosimilars: Recent advances in analytical characterization and clinical implications.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Dec 16;1089:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.08.044. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31627805 Review.
Cited by
-
NEU1-Mediated Extracellular Vesicle Glycosylation in Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanistic Insights into Intercellular Communication and Therapeutic Targeting.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;18(6):921. doi: 10.3390/ph18060921. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573316 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaffe GJ; Dick AD; Brézin AP; Nguyen QD; Thorne JE; Kestelyn P; Barisani-Asenbaur T; Franco P; Heiligenhaus A; Scales D; Chu DS; Camez A; Kwatra NV; Song AP; Kron M; Tari S; Schuler EB Adalimumab in Patients with Active Noninfectious Uveitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375 (10), 932–943. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509852 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

