Self-regulating CAR-T cells modulate cytokine release syndrome in adoptive T-cell therapy
- PMID: 38607370
- PMCID: PMC11010356
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20221988
Self-regulating CAR-T cells modulate cytokine release syndrome in adoptive T-cell therapy
Abstract
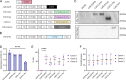
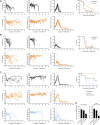
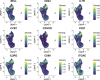
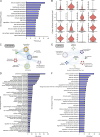
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a frequently observed side effect of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy. Here, we report self-regulating T cells that reduce CRS severity by secreting inhibitors of cytokines associated with CRS. With a humanized NSG-SGM3 mouse model, we show reduced CRS-related toxicity in mice treated with CAR-T cells secreting tocilizumab-derived single-chain variable fragment (Toci), yielding a safety profile superior to that of single-dose systemic tocilizumab administration. Unexpectedly, Toci-secreting CD19 CAR-T cells exhibit superior in vivo antitumor efficacy compared with conventional CD19 CAR-T cells. scRNA-seq analysis of immune cells recovered from tumor-bearing humanized mice revealed treatment with Toci-secreting CD19 CAR-T cells enriches for cytotoxic T cells while retaining memory T-cell phenotype, suggesting Toci secretion not only reduces toxicity but also significantly alters the overall T-cell composition. This approach of engineering T cells to self-regulate inflammatory cytokine production is a clinically compatible strategy with the potential to simultaneously enhance safety and efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy for cancer.
© 2024 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: M.-Y. Lin and Y.Y. Chen are inventors of a patent (US 11,701,384) whose value may be affected by the publication of this work. Y.Y. Chen holds several patent applications in the area of CAR-T cell therapy. Y.Y. Chen is a founder of, holds equity in, and receives consulting fees from ImmPACT Bio. Y.Y. Chen is a member of the scientific advisory board of and holds equity in Catamaran Bio, Notch Therapeutics, Pluto Immunotherapeutics, Prime Medicine, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and Waypoint Bio. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures










References
-
- Abramson, J.S., Palomba M.L., Gordon L.I., Lunning M.A., Wang M., Arnason J., Mehta A., Purev E., Maloney D.G., Andreadis C., et al. . 2020. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 396:839–852. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31366-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alcantara, M., Houillier C., Blonski M., Rubio M.T., Willems L., Rascalou A.W., Le Garff-Tavernier M., Maloum K., Bravetti C., Souchet L., et al. . 2022. CAR T-cell therapy in primary central nervous system lymphoma: The clinical experience of the French LOC network. Blood. 139:792–796. 10.1182/blood.2021012932 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh, D., Wong R.A., Yang X., Wang D., Pecoraro J.R., Kuo C.F., Aguilar B., Qi Y., Ann D.K., Starr R., et al. . 2019. IL15 enhances CAR-T cell antitumor activity by reducing mTORC1 activity and preserving their stem cell memory phenotype. Cancer Immunol. Res. 7:759–772. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0466 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle, P.A., Ding J., Patel E., Thorausch N., Horton H., Gierut J., Scarfo I., Choudhary R., Kiner O., Krishnamurthy J., et al. . 2019. Synthetic TRuC receptors engaging the complete T cell receptor for potent anti-tumor response. Nat. Commun. 10:2087. 10.1038/s41467-019-10097-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

