Updated component analysis method for naturally occurring sophorolipids from Starmerella bombicola
- PMID: 38607413
- PMCID: PMC11009742
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-024-13138-x
Updated component analysis method for naturally occurring sophorolipids from Starmerella bombicola
Abstract
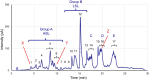
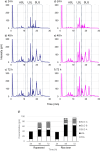
Sophorolipids (SLs) are promising glycolipid biosurfactants as they are easily produced and functional. SLs from microorganisms are comprised of mixtures of multiple derivatives that have different structures and properties, including well-known acidic and lactonic SL (ASLs and LSLs, respectively). In this study, we established a method for analyzing all SL derivatives in the products of Starmerella bombicola, a typical SL-producing yeast. Detailed component analyses of S. bombicola products were carried out using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Methanol was used as the eluent as it is a good solvent for all SL derivatives. With this approach, it was possible to not only quantify the ratio of the main components of ASL, LSL, and SL glycerides but also confirm trace components such as SL mono-glyceride and bola-form SL (sophorose at both ends); notably, this is the first time these components have been isolated and identified successfully in naturally occurring SLs. In addition, our results revealed a novel SL derivative in which a fatty acid is bonded in series to the ASL, which had not been reported previously. Using the present analysis method, it was possible to easily track compositional changes in the SL components during culture. Our results showed that LSL and ASL are produced initially and that SL glycerides accumulate from the middle stage during the fermentation process. KEY POINTS: • An easy and detailed component analysis method for sophorolipids (SLs) is introduced. • Multiple SL derivatives were identified different from known SLs. • A novel hydrophobic acidic SL was isolated and characterized.
Keywords: Starmerella bombicola; Biosurfactant; Component analysis; Glycolipid; LC–MS analysis; Sophorolipid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Revision of the sophorolipid biosynthetic pathway in Starmerella bombicola based on new insights in the substrate profile of its lactone esterase.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Jun 27;17(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02533-1. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 38937850 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and importance of mitochondrial citrate carriers and ATP citrate lyase for glycolipid production in Starmerella bombicola.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jul;104(14):6235-6248. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10702-z. Epub 2020 May 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32474798
-
Reduced-Cost Production of Sophorolipids by Starmerella bombicola CGMCC1576 Grown on Cottonseed Molasses and Cottonseed Oil-Based Medium.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5759. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065759. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982832 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in sophorolipid-producing strain performance improvement and fermentation optimization technology.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;104(24):10325-10337. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10964-7. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33097965 Review.
-
Sophorolipids bioproduction in the yeast Starmerella bombicola: Current trends and perspectives.Bioresour Technol. 2022 Feb;346:126593. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126593. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Bioresour Technol. 2022. PMID: 34942344 Review.
Cited by
-
Valorization of oil refinery by-products: production of sophorolipids utilizing fatty acid distillates and their potential antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and antifungal activities.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 10;40(11):344. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04144-2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39384621
-
Bubbling insights: unveiling the true sophorolipid biosynthetic pathway by Starmerella bombicola.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Aug 14;17(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02557-7. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 39143561 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Based Surfactants and Biosurfactants: An Overview and Main Characteristics.Molecules. 2025 Feb 13;30(4):863. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040863. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davila AM, Marchal R, Monin N, Vandecasteele JP (1993) Identification and determination of individual sophorolipids in fermentation products by gradient elution high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light-scattering detection. J Chromatogr 648:139–149. 10.1016/0021-9673(93)83295-4 - PubMed
-
- Díaz De Rienzo MA, Banat IM, Dolman B, Winterburn J, Martin PJ (2015) Sophorolipid biosurfactants: possible uses as antibacterial and antibiofilm agent. N Biotechnol 32:720–726. 10.1016/j.nbt.2015.02.009 - PubMed
-
- Dierickx S, Castelein M, Remmery J, Clercq VD, Lodens S, Baccile N, Maeseneire SLD, Roelants SLKW, Soetaert WK (2022) From bumblebee to bioeconomy: recent developments and perspectives for sophorolipid biosynthesis. Biotechnol Adv 54:10778. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107788 - PubMed
-
- Dolman BM, Kaisermann C, Martin PJ, Winterburn JB (2017) Integrated sophorolipid production and gravity separation. Process Biochem 54:162–171. 10.1016/j.procbio.2016.12.021
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

