Application of the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society Spirometry Standards and Race-Neutral Equations in the COPDGene Study
- PMID: 38607551
- PMCID: PMC11622435
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202311-2145OC
Application of the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society Spirometry Standards and Race-Neutral Equations in the COPDGene Study
Abstract
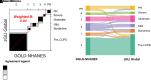
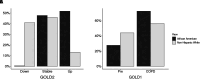
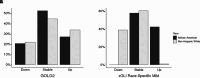
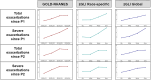
Rationale: For spirometry interpretation, the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and American Thoracic Society (ATS) recommend using z-scores, and the ATS has recommended using Global Lung Initiative (GLI) "Global" race-neutral reference equations. However, these recommendations have been variably implemented, and the impact has not been widely assessed in clinical or research settings. Objectives: To evaluate the ERS/ATS classification of airflow obstruction severity. Methods: In COPDGene (Genetic Epidemiology of COPD Study) (N = 10,108), airflow obstruction has been defined by an FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70, with spirometric severity graded from class 1 to class 4 based on race-specific percent predicted (pp) FEV1 cutoff points as recommended by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). We compared the GOLD approach, using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III race-specific equations, versus the application of GLI Global equations using the ERS/ATS definition of airflow obstruction as an FEV1/FVC ratio below the lower limit of normal and z-score-based FEV1 cutoff points of -1.645, -2.5, and -4 ("zGLI Global"). We tested the four-tier severity scheme for association with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease outcomes. Measurements and Main Results: The lowest agreement between ERS/ATS with zGLI Global and the GOLD classification was observed in individuals with milder disease (56.9% and 42.5% in GOLD stages 1 and 2, respectively), and race was a major determinant of redistribution. After adjustment for relevant covariates, zGLI Global distinguished all-cause mortality risk between normal spirometry and the first grade of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.44; P = 0.014) and showed a linear increase in exacerbation rates with increasing disease severity in comparison with GOLD. Conclusions: The zGLI Global severity classification outperformed the GOLD criteria in the discrimination of survival, exacerbations, and imaging characteristics.
Keywords: COPD; ethnicity; pulmonary function tests; survival analysis.
Figures
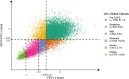
Comment in
-
Race-Neutral z-Score Classification of Airflow Obstruction: A Measured Step Forward.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Dec 1;210(11):1287-1289. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202404-0873ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38820133 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lung function testing: selection of reference values and interpretative strategies. American Thoracic Society. Am Rev Respir Dis . 1991;144:1202–1218. - PubMed
-
- Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J . 2005;26:948–968. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

