TIMAHAC: Streamlined Tandem IMAC-HILIC Workflow for Simultaneous and High-Throughput Plant Phosphoproteomics and N-glycoproteomics
- PMID: 38608839
- PMCID: PMC11098956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100762
TIMAHAC: Streamlined Tandem IMAC-HILIC Workflow for Simultaneous and High-Throughput Plant Phosphoproteomics and N-glycoproteomics
Abstract
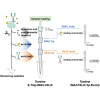
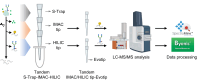
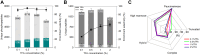
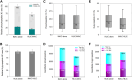
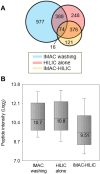
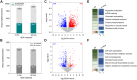
Protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) are crucial in plant cellular processes, particularly in protein folding and signal transduction. N-glycosylation and phosphorylation are notably significant PTMs, playing essential roles in regulating plant responses to environmental stimuli. However, current sequential enrichment methods for simultaneous analysis of phosphoproteome and N-glycoproteome are labor-intensive and time-consuming, limiting their throughput. Addressing this challenge, this study introduces a novel tandem S-Trap-IMAC-HILIC (S-Trap: suspension trapping; IMAC: immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography; HILIC: hydrophilic interaction chromatography) strategy, termed TIMAHAC, for simultaneous analysis of plant phosphoproteomics and N-glycoproteomics. This approach integrates IMAC and HILIC into a tandem tip format, streamlining the enrichment process of phosphopeptides and N-glycopeptides. The key innovation lies in the use of a unified buffer system and an optimized enrichment sequence to enhance efficiency and reproducibility. The applicability of TIMAHAC was demonstrated by analyzing the Arabidopsis phosphoproteome and N-glycoproteome in response to abscisic acid (ABA) treatment. Up to 1954 N-glycopeptides and 11,255 phosphopeptides were identified from Arabidopsis, indicating its scalability for plant tissues. Notably, distinct perturbation patterns were observed in the phosphoproteome and N-glycoproteome, suggesting their unique contributions to ABA response. Our results reveal that TIMAHAC offers a comprehensive approach to studying complex regulatory mechanisms and PTM interplay in plant biology, paving the way for in-depth investigations into plant signaling networks.
Keywords: ABA signaling; Arabidopsis thaliana; HILIC; IMAC; N-glycoproteomics; phosphoproteomics.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Chong L., Hsu C.C., Zhu Y. Advances in mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics for elucidating abscisic acid signaling and plant responses to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2022;73:6547–6557. - PubMed
-
- Veit C., Vavra U., Strasser R. N-Glycosylation and plant cell growth. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015;1242:183–194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

