A brief history of the Feulgen reaction
- PMID: 38609528
- PMCID: PMC11227455
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-024-02279-9
A brief history of the Feulgen reaction
Abstract
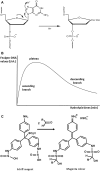
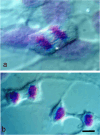
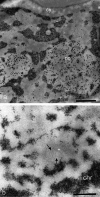
One hundred years ago, Robert Feulgen published a landmark paper in which he described the first method to stain DNA in cells and tissues. Although a century has passed since the discovery by Feulgen and Rossenbeck, the chemical reaction still exerts an important influence in current histochemical studies. Its contribution in diverse fields, spanning from biomedicine to plant biology, has paved the way for the most significant studies that constitute our current knowledge. The possibility to specifically explore the DNA in cell nuclei while quantifying its content makes it a contemporary and timeless method. Indeed, many histocytochemical studies following the 1924 paper have led to a deep understanding of genome organization in general as well as several specific mechanisms (e.g. DNA duplication or tumour pathology) that, nowadays, constitute some of the most fundamental pillars in biological investigations. In this review, we discuss the chemistry and application of the Feulgen reaction to both light and electron microscopy.
Keywords: Electron microscopy; Feulgen reaction; Light microscopy; Osmium ammine; Schiff-type reagent.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Feulgen reaction 75 years on.Histochem Cell Biol. 1999 May;111(5):345-58. doi: 10.1007/s004180050367. Histochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10403113 Review.
-
Osmium Ammine for Staining DNA in Electron Microscopy.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1560:261-267. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6788-9_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28155160
-
The Feulgen reaction: A brief review and new perspectives.Acta Histochem. 2017 Jul;119(6):603-609. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Acta Histochem. 2017. PMID: 28739089 Review.
-
Activation of osmium ammine by SO2-generating chemicals for EM Feulgen-type staining of DNA.Eur J Histochem. 1995;39(2):101-6. Eur J Histochem. 1995. PMID: 7549012
-
Distribution of DNA, nuclear micro-heterogeneities and compaction of the chromatin in rabbit epididymal spermatozoa. Ultrastructural evaluation of the Feulgen-like technique using osmium ammine.Reprod Nutr Dev. 1994;34(3):261-72. doi: 10.1051/rnd:19940308. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1994. PMID: 7519430
Cited by
-
Nuclear morphology explained through digital morphometry: differentiating nuclear features across the three histological grades in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024 Jul-Sep;65(3):421-431. doi: 10.47162/RJME.65.3.04. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024. PMID: 39529335 Free PMC article.
-
Seeing genomes.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Jul;162(1-2):1-2. doi: 10.1007/s00418-024-02301-0. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38850309 No abstract available.
References
-
- Biggiogera M. Unusual ultrastructural features of chromatin in mouse sperm cells after DNA staining with osmium ammines. Bas Appl Histochem. 1986;30:501–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

