Tumor-targeted PROTAC prodrug nanoplatform enables precise protein degradation and combination cancer therapy
- PMID: 38609561
- PMCID: PMC11272941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-024-01266-z
Tumor-targeted PROTAC prodrug nanoplatform enables precise protein degradation and combination cancer therapy
Abstract
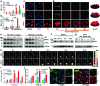
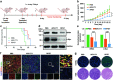
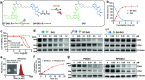
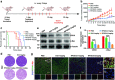
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) have emerged as revolutionary anticancer therapeutics that degrade disease-causing proteins. However, the anticancer performance of PROTACs is often impaired by their insufficient bioavailability, unsatisfactory tumor specificity and ability to induce acquired drug resistance. Herein, we propose a polymer-conjugated PROTAC prodrug platform for the tumor-targeted delivery of the most prevalent von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)- and cereblon (CRBN)-based PROTACs, as well as for the precise codelivery of a degrader and conventional small-molecule drugs. The self-assembling PROTAC prodrug nanoparticles (NPs) can specifically target and be activated inside tumor cells to release the free PROTAC for precise protein degradation. The PROTAC prodrug NPs caused more efficient regression of MDA-MB-231 breast tumors in a mouse model by degrading bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) or cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) with decreased systemic toxicity. In addition, we demonstrated that the PROTAC prodrug NPs can serve as a versatile platform for the codelivery of a PROTAC and chemotherapeutics for enhanced anticancer efficiency and combination benefits. This study paves the way for utilizing tumor-targeted protein degradation for precise anticancer therapy and the effective combination treatment of complex diseases.
Keywords: combination therapy; precise protein degradation; proteolysis-targeting chimeras; triple-negative breast cancer; tumor-targeted delivery.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of a Potent, selective and orally bioavailable CDK9 degrader for targeting transcription regulation in Triple-Negative breast cancer.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Dec;153:107876. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107876. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39406109
-
Hijacking the MDM2 E3 Ligase with Novel BRD4-Targeting Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras in Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Chembiochem. 2025 Jul 11;26(13):e202500133. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500133. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40317844 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-sensitive macrocycle inclusion complexes for targeted protein degradation.J Control Release. 2025 Aug 10;384:113921. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113921. Epub 2025 May 30. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 40451554
-
PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) Estrogen Receptor Degraders for Treatment of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer.Target Oncol. 2025 May;20(3):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s11523-025-01137-5. Epub 2025 May 6. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40327300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic therapy meets targeted protein degradation: HDAC-PROTACs in cancer treatment.Future Med Chem. 2025 Jul;17(14):1725-1737. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2533113. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40667573 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) for Immunotherapy: Understanding Proteolysis Targeting Chimera-Driven Ubiquitin-Proteasome Interactions.Bioconjug Chem. 2024 Aug 21;35(8):1089-1115. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.4c00253. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Bioconjug Chem. 2024. PMID: 38990186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of dual aptamers-functionalized c-MET PROTAC degraders for targeted therapy of osteosarcoma.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(1):103-121. doi: 10.7150/thno.99588. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39744222 Free PMC article.
-
Precision-engineered PROTACs minimize off-tissue effects in cancer therapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Nov 22;11:1505255. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1505255. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39649701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prodrug Strategy for PROTACs: High Efficiency and Low Toxicity.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 5;10(23):23926-23942. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01241. eCollection 2025 Jun 17. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40547641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanomedicine: Cutting-Edge Research on Nano-PROTAC Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Aug 10;17(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17081037. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40871058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

