Significance of early diagnosis and surgical management in treating Mycobacterium immunogenum-related pyogenic extensor tenosynovitis: a case report
- PMID: 38609847
- PMCID: PMC11010399
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09249-5
Significance of early diagnosis and surgical management in treating Mycobacterium immunogenum-related pyogenic extensor tenosynovitis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are environmental organisms that are increasingly contributing to human infections. Mycobacterium immunogenum, a variant of NTM discovered in 2001, is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that exhibits multidrug resistance. Reports of infections caused by this organism, particularly tenosynovitis in the musculoskeletal system, are limited.
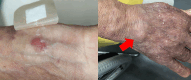
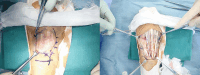
Case presentation: A 71-year-old female with vesicular pemphigus, undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, presented with a progressively enlarging tumour on the dorsum of her right hand, along with erythematous papules that extended across her right forearm. The specimens of skin tissues and blood cultures revealed the presence of M. immunogenum. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation led to the diagnosis of pyogenic extensor tenosynovitis. A multidrug regimen, comprising amikacin and clarithromycin, was initiated, followed by synovectomy. The patient underwent a course of 180 days of antimicrobial therapy and demonstrated no signs of disease recurrence one year after treatment completion.
Conclusion: Early diagnosis and surgical intervention are crucial to prevent the adverse prognostic implications of pyogenic extensor tenosynovitis caused by M. immunogenum. Effective management requires precise microbial identification and susceptibility testing, necessitating collaborative engagement with microbiological laboratories.
Keywords: Mycobacterium immunogenum; Nontuberculous mycobacterium; Pyogenic extensor tenosynovitis; Rapidly growing mycobacteria.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Refractory tenosynovitis caused by Mycobacterium virginiense required repeated debridement: A case report and literature review.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Sep;113(1):116874. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2025.116874. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40328019 Review.
-
A refractory tenosynovitis of the wrist: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2022 Feb 21;16(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03278-x. J Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35184751 Free PMC article.
-
Extensor Tenosynovitis due to Mycobacterium marseillense Infection in a Renal Transplant Recipient.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021 Jan 12;5(1):e20.00047. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-20-00047. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33448712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium Immunogenum Flexor Tenosynovitis: A Case Report.J Wrist Surg. 2021 Jun;10(3):241-244. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1715803. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Wrist Surg. 2021. PMID: 34109068 Free PMC article.
-
Flexor Tenosynovitis Caused by Mycobacterium arupense: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.JBJS Case Connect. 2020 Jul-Sep;10(3):e20.00033. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.CC.20.00033. JBJS Case Connect. 2020. PMID: 32910569 Review.
Cited by
-
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pneumonia Caused by Mycobacterium immunogenum: A Case Report and Literature Review.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Apr 13;18:1859-1865. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S512539. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40247892 Free PMC article.
-
A case of culture-proven cutaneous atypical mycobacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium immunogenum.JAAD Case Rep. 2025 Mar 10;60:160-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2025.02.021. eCollection 2025 Jun. JAAD Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40510777 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilson RW, Steingrube VA, Böttger EC, Springer B, Brown-Elliott BA, Vincent V, et al. Mycobacterium immunogenum sp. nov., a novel species related to Mycobacterium abscessus and associated with clinical disease, pseudo-outbreaks and contaminated metalworking fluids: an international cooperative study on mycobacterial taxonomy. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:1751–64. doi: 10.1099/00207713-51-5-1751. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Zamora E, Sanz-Robles H, Elosua-Gonzalez M, Rodriguez-Vasquez X, Lopez-Estebaranz JL. Cutaneous infection due to Mycobacterium immunogenum: an European case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030qt9zg5r07t. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

