A combined nomogram based on radiomics and hematology to predict the pathological complete response of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38609892
- PMCID: PMC11015586
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12239-0
A combined nomogram based on radiomics and hematology to predict the pathological complete response of neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: To predict pathological complete response (pCR) in patients receiving neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy (nICT) for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), we explored the factors that influence pCR after nICT and established a combined nomogram model.
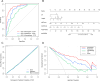
Methods: We retrospectively included 164 ESCC patients treated with nICT. The radiomics signature and hematology model were constructed utilizing least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression, and the radiomics score (radScore) and hematology score (hemScore) were determined for each patient. Using the radScore, hemScore, and independent influencing factors obtained through univariate and multivariate analyses, a combined nomogram was established. The consistency and prediction ability of the nomogram were assessed utilizing calibration curve and the area under the receiver operating factor curve (AUC), and the clinical benefits were assessed utilizing decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: We constructed three predictive models.The AUC values of the radiomics signature and hematology model reached 0.874 (95% CI: 0.819-0.928) and 0.772 (95% CI: 0.699-0.845), respectively. Tumor length, cN stage, the radScore, and the hemScore were found to be independent factors influencing pCR according to univariate and multivariate analyses (P < 0.05). A combined nomogram was constructed from these factors, and AUC reached 0.934 (95% CI: 0.896-0.972). DCA demonstrated that the clinical benefits brought by the nomogram for patients across an extensive range were greater than those of other individual models.
Conclusions: By combining CT radiomics, hematological factors, and clinicopathological characteristics before treatment, we developed a nomogram model that effectively predicted whether ESCC patients would achieve pCR after nICT, thus identifying patients who are sensitive to nICT and assisting in clinical treatment decision-making.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Hematology; Neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy; Nomogram; Pathological complete response; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CT-based delta-radiomics for predicting pathological response to neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a multicenter study.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Dec 3;24(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01503-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39627736 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based delta-radiomics nomogram to predict pathological complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.J Transl Med. 2024 Jun 18;22(1):579. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05392-4. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38890720 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram based on pretreatment CT radiomics features for predicting complete response to chemoradiotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Oct 29;15(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01692-3. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33121507 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of systemic immune-inflammation index for pathological complete response in patients receiving neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 4;9:1091601. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1091601. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684142 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting anastomotic leak in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy using a nomogram based on CT radiomic and clinicopathologic factors.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 15;25(1):484. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13884-9. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40089723 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CT-radiomics combined with inflammatory indicators for prediction of progression free survival of resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 May 10;15(1):16287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01240-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40348786 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel-level radiomics and deep learning for predicting pathologic complete response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after neoadjuvant immunotherapy and chemotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Mar 15;13(3):e011149. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-011149. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40090670 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and MELD score for short-term survival of patients with HBV-DeCi.Biomark Med. 2025 Jan;19(2):43-49. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2448112. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Biomark Med. 2025. PMID: 39781609
-
Dynamic radiological features predict pathological response after neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2024 May 18;22(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05291-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38762454 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based delta-radiomics for predicting pathological response to neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a multicenter study.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Dec 3;24(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01503-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39627736 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

