Transcriptomic and targeted metabolomic analyses provide insights into the flavonoids biosynthesis in the flowers of Lonicera macranthoides
- PMID: 38609923
- PMCID: PMC11015657
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-024-00846-5
Transcriptomic and targeted metabolomic analyses provide insights into the flavonoids biosynthesis in the flowers of Lonicera macranthoides
Erratum in
-
Correction: Transcriptomic and targeted metabolomic analyses provide insights into the flavonoids biosynthesis in the flowers of Lonicera macranthoides.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 May 20;24(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00860-7. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38769530 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Flavonoids are one of the bioactive ingredients of Lonicera macranthoides (L. macranthoides), however, their biosynthesis in the flower is still unclear. In this study, combined transcriptomic and targeted metabolomic analyses were performed to clarify the flavonoids biosynthesis during flowering of L. macranthoides.
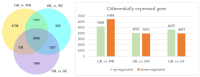
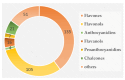
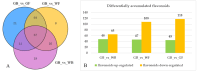
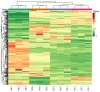
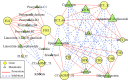
Results: In the three sample groups, GB_vs_WB, GB_vs_WF and GB_vs_GF, there were 25, 22 and 18 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in flavonoids biosynthetic pathway respectively. A total of 339 flavonoids were detected and quantified at four developmental stages of flower in L. macranthoides. In the three sample groups, 113, 155 and 163 differentially accumulated flavonoids (DAFs) were detected respectively. Among the DAFs, most apigenin derivatives in flavones and most kaempferol derivatives in flavonols were up-regulated. Correlation analysis between DEGs and DAFs showed that the down-regulated expressions of the CHS, DFR, C4H, F3'H, CCoAOMT_32 and the up-regulated expressions of the two HCTs resulted in down-regulated levels of dihydroquercetin, epigallocatechin and up-regulated level of kaempferol-3-O-(6''-O-acetyl)-glucoside, cosmosiin and apigenin-4'-O-glucoside. The down-regulated expressions of F3H and FLS decreased the contents of 7 metabolites, including naringenin chalcone, proanthocyanidin B2, B3, B4, C1, limocitrin-3,7-di-O-glucoside and limocitrin-3-O-sophoroside.
Conclusion: The findings are helpful for genetic improvement of varieties in L.macranthoides.
Keywords: Lonicera macranthoides; Anthocyanin; Flavone; Flavonoid biosynthesis; Flavonol; Flower; Targeted metabolome; Transcriptome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Carotenoid metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses provide insights into the flower color transition in Lonicera macranthoides.BMC Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12896-025-01007-y. BMC Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40634871 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of flower petals color transition in different phenotype of Lonicera macranthoides.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jul 10;16:1605238. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1605238. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40708580 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling reveals molecular regulatory network involved in flower development and phenotypic changes in two Lonicera macranthoides varieties.3 Biotech. 2024 Jul;14(7):174. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04019-1. Epub 2024 Jun 5. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38855147 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Dietary flavonoid for preventing colorectal neoplasms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;2012(8):CD009350. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009350.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22895989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LoniComp: a platform for gene function comparison and analysis between Lonicera japonica and Lonicera macranthoides.BMC Genomics. 2025 Apr 1;26(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11507-y. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40170166 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Transcriptomic and targeted metabolomic analyses provide insights into the flavonoids biosynthesis in the flowers of Lonicera macranthoides.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 May 20;24(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00860-7. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38769530 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ultrasonic/compound enzyme extraction, comparative characterisation and biological activity of Lonicera macranthoides polysaccharides.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Mar;114:107259. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107259. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39933310 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid identification of Lonicera japonica via Proofman-LMTIA technology.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 6;15(1):7913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91797-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40050336 Free PMC article.
-
Carotenoid metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses provide insights into the flower color transition in Lonicera macranthoides.BMC Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12896-025-01007-y. BMC Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40634871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang J, Xu BH, Pan X. Study on the distinguishing points of Honeysuckle and Lonicerae Flos. Beijing J Tradit Chin Med. 2019;38:73–6.
-
- Treutter D. Significance of flavonoids in plant resistance and enhancement of their biosynthesis. Plant Biol. 2005; 7, 581–91. PMID:16388461. 10.1055/s-2005-873009 - PubMed
-
- Bai ZJ, Ren QL, Feng TT, Zhao Z, Zhou Y, Lin B. Study on Lonicera macranthoides Hand-Mazz anti-inflammatory activity based on inflammatory cell model. Chin Med J Res Prac. 2015;29:35–9.
-
- Wang ZH, Zhou XR, Cheng HZ, Wang Z, Tong QZ, Zhou RB* Liu X.D*. Prediction of antioxidant and antibacterial quality markers of Lonicerae Flos based on multivariate statistical analysis. J Hunan Univ Chin Med. 2022;42:1105–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

