Microbial bionic nano-aromatic drugs for prevention of depression induced by chronic stress
- PMID: 38609944
- PMCID: PMC11015588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02382-y
Microbial bionic nano-aromatic drugs for prevention of depression induced by chronic stress
Abstract
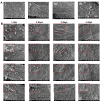
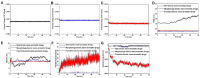
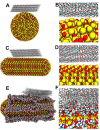
Depression is a mood disorder mainly clinically characterized by significant and persistent low spirits. Chronic stress is the leading cause of depression. However, traditional medicine has severe side effects in treating depression, ineffective treatment, and easy recurrence. Therefore, it is of great significance to prevent depression in the environment of chronic stress. In this study, aromatherapy was used for the prevention of depression. To solve the defects of intense volatility and inconvenience in using essential oils, we designed bionic nano-aromatic drugs and adhered them to the wallpaper. Inspired by the moldy wallpaper, we successively prepared the morphology-bionic nano-aromatic drugs, the function-bionic nano-aromatic drugs, and the bionic plus nano-aromatic drugs by referring to the morphology of microorganisms and substances in bacterial biofilms. Bionic nano-aromatic drugs remarkably promoted their adhesion on wallpaper. Molecular dynamics simulation explored its molecular mechanism. The essential oils, which were slowly released from the bionic nano-aromatic drugs, showed excellent biosecurity and depression prevention. These sustainedly released essential oils could significantly increase monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain under a chronic stress environment and had excellent neuroprotection. Besides, the bionic nano-aromatic drugs with simple preparation process and low cost had excellent application potential.
Keywords: Aromatherapy; Chronic stress; Microbial bionic nano-aromatic drugs; Prevention of depression; Sustain release of essential oils.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Thase ME. Depression, sleep, and antidepressants. J Clin Psychiat. 1998;59:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Orsolini L, Valchera A, Vecchiotti R, Panichi M, Berardis DD. Psychosis and polydrug abuse in a patient with Dandy-Walker variant. Eur Psychiat. 2016;33:S310.
-
- Zhu SL, Lie LJ, Li Y, Cao WY. Macrophage related cytokine expressions in depression mouse model induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017;30:1951–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

