Neo-epitope detection identifies extracellular matrix turnover in systemic inflammation and sepsis: an exploratory study
- PMID: 38609959
- PMCID: PMC11010428
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-024-04904-4
Neo-epitope detection identifies extracellular matrix turnover in systemic inflammation and sepsis: an exploratory study
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is associated with high morbidity and mortality, primarily due to systemic inflammation-induced tissue damage, resulting organ failure, and impaired recovery. Regulated extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis in health and in response to disease-related changes in the tissue microenvironment. Conversely, uncontrolled turnover can contribute to tissue damage. Systemic Inflammation is implicated to play a role in the regulation of ECM turnover, but the relationship between the two is largely unclear.
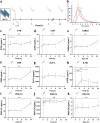
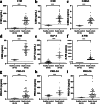
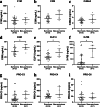
Methods: We performed an exploratory study in 10 healthy male volunteers who were intravenously challenged with 2 ng/kg lipopolysaccharide (LPS, derived from Escherichia coli) to induce systemic inflammation. Plasma samples were collected before (T0) and after (T 1 h, 3 h, 6 h and 24 h) the LPS challenge. Furthermore, plasma was collected from 43 patients with septic shock on day 1 of ICU admission. Circulating neo-epitopes of extracellular matrix turnover, including ECM degradation neo-epitopes of collagen type I (C1M), type III (C3M), type IV (C4Ma3), and type VI (C6M), elastin (ELP-3) and fibrin (X-FIB), as well as the ECM synthesis neo-epitopes of collagen type III (PRO-C3), collagen type IV (PRO-C4) and collagen type VI (PRO-C6) were measured by ELISA. Patient outcome data were obtained from electronic patient records.
Results: Twenty-four hours after LPS administration, all measured ECM turnover neo-epitopes, except ELP-3, were increased compared to baseline levels. In septic shock patients, concentrations of all measured ECM neo-epitopes were higher compared to healthy controls. In addition, concentrations of C6M, ELP-3 and X-FIB were higher in patients with septic shock who ultimately did not survive (N = 7) compared to those who recovered (N = 36).
Conclusion: ECM turnover is induced in a model of systemic inflammation in healthy volunteers and was observed in patients with septic shock. Understanding interactions between systemic inflammation and ECM turnover may provide further insight into mechanisms underlying acute and persistent organ failure in sepsis.
Keywords: Collagen; Extracellular matrix turnover; Human endotoxemia; Neo-epitope; Sepsis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JKB receives unrestricted research funds from Boehringer Ingelheim paid directly to the Institute, unrelated to this work. DJL and JMBS are full-time employees and stockholders at Nordic Bioscience.
Figures
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

