Dysregulation of neuroprotective lipoxin pathway in astrocytes in response to cytokines and ocular hypertension
- PMID: 38610040
- PMCID: PMC11010376
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-024-01767-2
Dysregulation of neuroprotective lipoxin pathway in astrocytes in response to cytokines and ocular hypertension
Abstract
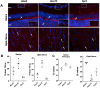
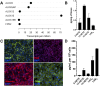
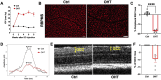
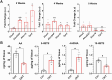
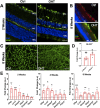
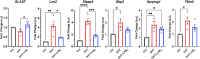
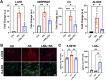
Glaucoma leads to vision loss due to retinal ganglion cell death. Astrocyte reactivity contributes to neurodegeneration. Our recent study found that lipoxin B4 (LXB4), produced by retinal astrocytes, has direct neuroprotective actions on retinal ganglion cells. In this study, we aimed to investigate how the autacoid LXB4 influences astrocyte reactivity in the retina under inflammatory cytokine-induced activation and during ocular hypertension. The protective activity of LXB4 was investigated in vivo using the mouse silicone-oil model of chronic ocular hypertension. By employing a range of analytical techniques, including bulk RNA-seq, RNAscope in-situ hybridization, qPCR, and lipidomic analyses, we discovered the formation of lipoxins and expression of the lipoxin pathway in rodents (including the retina and optic nerve), primates (optic nerve), and human brain astrocytes, indicating the presence of this neuroprotective pathway across various species. Findings in the mouse retina identified significant dysregulation of the lipoxin pathway in response to chronic ocular hypertension, leading to an increase in 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) activity and a decrease in 15-LOX activity. This dysregulation was coincident with a marked upregulation of astrocyte reactivity. Reactive human brain astrocytes also showed a significant increase in 5-LOX. Treatment with LXB4 amplified the lipoxin biosynthetic pathway by restoring and amplifying the generation of another member of the lipoxin family, LXA4, and mitigated astrocyte reactivity in mouse retinas and human brain astrocytes. In conclusion, the lipoxin pathway is functionally expressed in rodents, primates, and human astrocytes, and is a resident neuroprotective pathway that is downregulated in reactive astrocytes. Novel cellular targets for LXB4's neuroprotective action are inhibition of astrocyte reactivity and restoration of lipoxin generation. Amplifying the lipoxin pathway is a potential target to disrupt or prevent astrocyte reactivity in neurodegenerative diseases, including retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma.
Keywords: Astrocyte reactivity; Glaucoma; Lipoxin B4; Lipoxygenase; Neurodegeneration; Optic nerve; Retina.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Dysregulation of Neuroprotective Lipoxin Pathway in Astrocytes in Response to Cytokines and Ocular Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 2:2023.06.22.546157. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.22.546157. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Apr 12;12(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01767-2. PMID: 37425861 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Regulation of disease-associated microglia in the optic nerve by lipoxin B4 and ocular hypertension.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00775-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39568070 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Diseases-Associated Microglia in the Optic Nerve by Lipoxin B4 and Ocular Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 28:2024.03.18.585452. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.18.585452. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00775-z. PMID: 38562864 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dysregulation of Neuroprotective Lipoxin Pathway in Astrocytes in Response to Cytokines and Ocular Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 2:2023.06.22.546157. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.22.546157. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Apr 12;12(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01767-2. PMID: 37425861 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Rho kinase inhibitor for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 10;6(6):CD013817. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013817.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35686679 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection for treatment of glaucoma in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 25;1(1):CD006539. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006539.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28122126 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lipidomic Analysis Reveals Drug-Induced Lipoxins in Glaucoma Treatment.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2025.01.24.634771. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.24.634771. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975338 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Regulation of disease-associated microglia in the optic nerve by lipoxin B4 and ocular hypertension.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00775-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39568070 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) as a Potential Drug for Diabetic Retinopathy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 21;61(2):177. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020177. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Diseases-Associated Microglia in the Optic Nerve by Lipoxin B4 and Ocular Hypertension.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 28:2024.03.18.585452. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.18.585452. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00775-z. PMID: 38562864 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

