Use of a Triaxial Accelerometer to Measure Changes in Gait Sway and Related Motor Function after Corrective Spinal Fusion Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity
- PMID: 38610688
- PMCID: PMC11012576
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13071923
Use of a Triaxial Accelerometer to Measure Changes in Gait Sway and Related Motor Function after Corrective Spinal Fusion Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity
Abstract
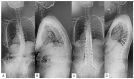
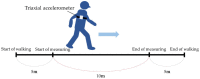
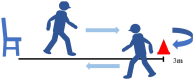
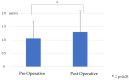
Background: Adult spinal deformity is a complex condition that causes lower back pain, causing spinal imbalance and discomfort in activities of daily life. After corrective spinal surgery, patients' gait and balance abilities might not revert to normalcy and they might be at increased risk of falling. Therefore, early evaluation of such a risk is imperative to prevent further complications such as a fall, or even worse, fractures in post-surgery ASD patients. However, there has been no report of an investigation of such early changes in gait sway before and after ASD surgery. This is a prospective to investigate changes in gait sway before and following ASD surgery, using accelerometers, and also to examine motor function related to postoperative gait sway. Methods: Twenty patients were included who underwent corrective surgery as treatment for ASD, from October 2019 to January 2023. Measurement parameters included a 10 m walking test and the timed up-and-go test (TUG), gait sway was evaluated using accelerometers (root mean square; RMS), and hip flexion and knee extension muscle strength were tested. RMS included RMS vertical: RMSV; RMS anterior posterior: RMSAP; RMS medial lateral: RMSML. The radiographic spinopelvic parameters were also evaluated preoperatively and postoperatively. p < 0.05 was noted as remarkably significant. Results: Preoperative and postoperative RMSV were 1.07 ± 0.6 and 1.31 ± 0.8, respectively (p < 0.05). RMSML significantly decreased from 0.33 ± 0.2 to 0.19 ± 0.1 postoperatively (p < 0.01). However, RMSAP did not change postoperatively (0.20 ± 0.2 vs. 0.14 ± 0.1, p > 0.05). Patients' one-month postoperative hip flexor muscle strength became significantly weaker (0.16 ± 0.04 vs. 0.10 ± 0.03 kgf/kg, p = 0.002), but TUG was maintained (11.6 ± 4.2 vs. 11.7 s, p = 0.305). RMSV was negatively correlated with quadriceps muscle strength and positively with TUG. RMSAP was negatively correlated with quadriceps muscle strength. All spinopelvic parameters became normal range after surgery. Conclusions: After corrective spinal fusion for ASD patients, the gait pattern improved significantly. Iliopsoas (hip flexor) and quadriceps femoris (knee extensor) muscles may play important roles for gait anterolateral and vertical swing, respectively.
Keywords: adult spinal deformity; gait sway; rehabilitation; spinal balance; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Hiroki Tomiyama was employed by the company Hashimoto Artificial Limb Manufacture Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Kondo R., Yamato Y., Nagafusa T., Mizushima T., Hasegawa T., Kobayashi S., Togawa D., Oe S., Kurosu K., Matsuyama Y. Effect of corrective long spinal fusion to the ilium on physical function in patients with adult spinal deformity. Eur. Spine J. 2017;26:2138–2145. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-4987-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi T., Tanaka M., Suthar H., Fujiwara Y., Uotani K., Arataki S., Yamauchi T., Sugyo A., Takamatsu K., Yasuda Y., et al. Chronological evaluation of gait ability and posture balance after adult spinal deformity surgery. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:4285. doi: 10.3390/app12094285. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

