Intracranial Efficacy of Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab, Carboplatin, and Paclitaxel in Real-World Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR or ALK Alterations
- PMID: 38610927
- PMCID: PMC11011096
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16071249
Intracranial Efficacy of Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab, Carboplatin, and Paclitaxel in Real-World Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR or ALK Alterations
Abstract
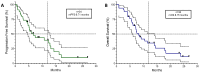
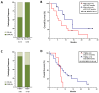
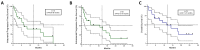
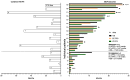
Contrary to Pemetrexed-containing chemo-immunotherapy studies, Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab, Carboplatin, and Paclitaxel (ABCP) treatment has consistently shown clinical benefit in prospective studies in patients with lung cancer and actionable mutations, where intracranial metastases are common. Here, we aimed to describe the real-life population of patients fit to receive ABCP after targeted therapy and quantify its clinical effect in patients with brain metastases. Patients treated in Cheshire and Merseyside between 2019 and 2022 were identified. Data were collected retrospectively. A total of 34 patients with actionable EGFR or ALK alterations had treatment with a median age of 59 years (range 32-77). The disease control rate was 100% in patients with PDL1 ≥ 1% (n = 10). In total, 19 patients (56%) had brain metastases before starting ABCP, 17 (50%) had untreated CNS disease, and 4 (22%) had PDL1 ≥ 1%. The median time to symptom improvement was 12.5 days (range 4-21 days), with 74% intracranial disease control rates and 89.5% synchronous intracranial (IC) and extracranial (EC) responses. IC median Progression Free Survival (mPFS) was 6.48 months, EC mPFS was 10.75 months, and median Overall Survival 11.47 months. ABCP in real-life patients with brain metastases (treated or untreated) was feasible and showed similar efficacy to that described in patients without actionable mutations treated with upfront chemo-immunotherapy.
Keywords: ALK; Atezolizumab; EGFR; PDL1; Paclitaxel; brain metastases; checkpoint inhibitor; immunotherapy; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
C.E. has received lecturing and travelling grants from Roche. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gillespie C.S., Mustafa M.A., Richardson G.E., Alam A.M., Lee K.S., Hughes D.M., Escriu C., Zakaria R. Genomic Alterations and the Incidence of Brain Metastases in Advanced and Metastatic NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023;18:1703–1713. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.06.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

