Immune Response and Metastasis-Links between the Metastasis Driver MACC1 and Cancer Immune Escape Strategies
- PMID: 38611008
- PMCID: PMC11010928
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16071330
Immune Response and Metastasis-Links between the Metastasis Driver MACC1 and Cancer Immune Escape Strategies
Abstract
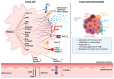
Metastasis remains the most critical factor limiting patient survival and the most challenging part of cancer-targeted therapy. Identifying the causal drivers of metastasis and characterizing their properties in various key aspects of cancer biology is essential for the development of novel metastasis-targeting approaches. Metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) is a prognostic and predictive biomarker that is now recognized in more than 20 cancer entities. Although MACC1 can already be linked with many hallmarks of cancer, one key process-the facilitation of immune evasion-remains poorly understood. In this review, we explore the direct and indirect links between MACC1 and the mechanisms of immune escape. Therein, we highlight the signaling pathways and secreted factors influenced by MACC1 as well as their effects on the infiltration and anti-tumor function of immune cells.
Keywords: MACC1; immune evasion; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kortüm B., Radhakrishnan H., Zincke F., Sachse C., Burock S., Keilholz U., Dahlmann M., Walther W., Dittmar G., Kobelt D., et al. Combinatorial treatment with statins and niclosamide prevents CRC dissemination by unhinging the MACC1-β-catenin-S100A4 axis of metastasis. Oncogene. 2022;41:4446–4458. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02407-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

