The Degree of Inulin Polymerization Is Important for Short-Term Amelioration of High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Rats
- PMID: 38611345
- PMCID: PMC11011263
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13071039
The Degree of Inulin Polymerization Is Important for Short-Term Amelioration of High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Rats
Erratum in
-
Correction: Ariaee et al. The Degree of Inulin Polymerization Is Important for Short-Term Amelioration of High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Rats. Foods 2024, 13, 1039.Foods. 2024 Dec 13;13(24):4030. doi: 10.3390/foods13244030. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39767129 Free PMC article.
Abstract
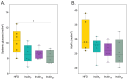
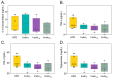
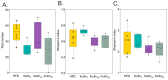
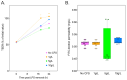
Inulin, a non-digestible polysaccharide, has gained attention for its prebiotic properties, particularly in the context of obesity, a condition increasingly understood as a systemic inflammatory state linked to gut microbiota composition. This study investigates the short-term protective effects of inulin with different degrees of polymerization (DPn) against metabolic health deterioration and gut microbiota alterations induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) in Sprague Dawley rats. Inulin treatments with an average DPn of 7, 14, and 27 were administered at 1 g/kg of bodyweight to HFD-fed rats over 21 days. Body weight, systemic glucose levels, and proinflammatory markers were measured to assess metabolic health. Gut microbiota composition was analyzed through 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The results showed that inulin27 significantly reduced total weight gain and systemic glucose levels, suggesting a DPn-specific effect on metabolic health. The study also observed shifts in gut microbial populations, with inulin7 promoting several beneficial taxa from the Bifidobacterium genera, whilst inducing a unique microbial composition compared to medium-chain (DPn 14) and long-chain inulin (DPn: 27). However, the impact of inulin on proinflammatory markers and lipid metabolism parameters was not statistically significant, possibly due to the short study duration. Inulin with a higher DPn has a more pronounced effect on mitigating HFD-induced metabolic health deterioration, whilst inulin7 is particularly effective at inducing healthy microbial shifts. These findings highlight the benefits of inulin as a dietary adjuvant in obesity management and the importance of DPn in optimizing performance.
Keywords: dysbiosis; fructooligosaccharides; gut microbiome; inulin; metabolic disease; obesity; prebiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Alsuhibani A., Alrasheed M., Gari M., Hincapie A.L., Guo J.J. Descriptive analysis of reported adverse events associated with anti-obesity medications using FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) databases 2013–2020. Pharm. Weekbl. 2022;44:172–179. doi: 10.1007/s11096-021-01330-2. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

